- Photoshop User Guide
- Introduction to Photoshop
- Photoshop and other Adobe products and services
- Photoshop on mobile (not available in mainland China)
- Photoshop on the iPad (not available in mainland China)
- Photoshop on the iPad | Common questions
- Get to know the workspace
- System requirements | Photoshop on the iPad
- Create, open, and export documents
- Add photos
- Work with layers
- Draw and paint with brushes
- Make selections and add masks
- Retouch your composites
- Work with adjustment layers
- Adjust the tonality of your composite with Curves
- Apply transform operations
- Crop and rotate your composites
- Rotate, pan, zoom, and reset the canvas
- Work with Type layers
- Work with Photoshop and Lightroom
- Get missing fonts in Photoshop on the iPad
- Japanese Text in Photoshop on the iPad
- Manage app settings
- Touch shortcuts and gestures
- Keyboard shortcuts
- Edit your image size
- Livestream as you create in Photoshop on the iPad
- Correct imperfections with the Healing Brush
- Create brushes in Capture and use them in Photoshop on the iPad
- Work with Camera Raw files
- Create and work with Smart Objects
- Adjust exposure in your images with Dodge and Burn
- Auto adjustment commands in Photoshop on the iPad
- Smudge areas in your images with Photoshop on the iPad
- Saturate or desaturate your images using Sponge tool
- Content aware fill for iPad
- Photoshop on the web (not available in mainland China)
- Photoshop (beta) (not available in mainland China)
- Generative AI (not available in mainland China)
- Common questions on generative AI in Photoshop
- Generative Fill in Photoshop on the desktop
- Generate Image with descriptive text prompts
- Generative Expand in Photoshop on the desktop
- Replace background with Generate background
- Get new variations with Generate Similar
- Select an AI model for generative control
- Generative Fill in Photoshop on the iPad
- Generative Expand in Photoshop on the iPad
- Generative AI features in Photoshop on the web
- Content authenticity (not available in mainland China)
- Cloud documents (not available in mainland China)
- Photoshop cloud documents | Common questions
- Photoshop cloud documents | Workflow questions
- Manage and work with cloud documents in Photoshop
- Upgrade cloud storage for Photoshop
- Unable to create or save a cloud document
- Solve Photoshop cloud document errors
- Collect cloud document sync logs
- Invite others to edit your cloud documents
- Share documents for review
- Workspace
- Workspace basics
- Preferences
- Learn faster with the Photoshop Discover Panel
- Create documents
- Place files
- Default keyboard shortcuts
- Customize keyboard shortcuts
- Tool galleries
- Performance preferences
- Contextual Task Bar
- Use tools
- Presets
- Grid and guides
- Touch gestures
- Use the Touch Bar with Photoshop
- Touch capabilities and customizable workspaces
- Technology previews
- Metadata and notes
- Place Photoshop images in other applications
- Rulers
- Show or hide non-printing Extras
- Specify columns for an image
- Undo and history
- Panels and menus
- Position elements with snapping
- Position with the Ruler tool
- Organize, share, and collaborate with Projects
- Refine Adobe Firefly generations
- Image and color basics
- How to resize images
- Work with raster and vector images
- Image size and resolution
- Acquire images from cameras and scanners
- Create, open, and import images
- View images
- Invalid JPEG Marker error | Opening images
- Viewing multiple images
- Customize color pickers and swatches
- High dynamic range images
- Match colors in your image
- Convert between color modes
- Color modes
- Erase parts of an image
- Blending modes
- Choose colors
- Customize indexed color tables
- Image information
- Distort filters are unavailable
- About color
- Color and monochrome adjustments using channels
- Choose colors in the Color and Swatches panels
- Sample
- Color mode or Image mode
- Color cast
- Add a conditional mode change to an action
- Add swatches from HTML CSS and SVG
- Bit depth and preferences
- Layers
- Layer basics
- Nondestructive editing
- Create and manage layers and groups
- Select, group, and link layers
- Place images into frames
- Layer opacity and blending
- Mask layers
- Apply Smart Filters
- Layer comps
- Move, stack, and lock layers
- Mask layers with vector masks
- Manage layers and groups
- Layer effects and styles
- Edit layer masks
- Extract assets
- Reveal layers with clipping masks
- Generate image assets from layers
- Work with Smart Objects
- Blending modes
- Combine multiple images into a group portrait
- Combine images with Auto-Blend Layers
- Align and distribute layers
- Copy CSS from layers
- Load selections from a layer or layer mask's boundaries
- Knockout to reveal content from other layers
- Selections
- Get started with selections
- Make selections in your composite
- Select and Mask workspace
- Select with the marquee tools
- Select with the lasso tools
- Adjust pixel selections
- Move, copy, and delete selected pixels
- Create a temporary quick mask
- Select a color range in an image
- Convert between paths and selection borders
- Channel basics
- Save selections and alpha channel masks
- Select the image areas in focus
- Duplicate, split, and merge channels
- Channel calculations
- Get started with selections
- Image adjustments
- Replace object colors
- Perspective warp
- Reduce camera shake blurring
- Healing brush examples
- Export color lookup tables
- Adjust image sharpness and blur
- Understand color adjustments
- Apply a Brightness/Contrast adjustment
- Adjust shadow and highlight detail
- Levels adjustment
- Adjust hue and saturation
- Adjust vibrance
- Adjust color saturation in image areas
- Make quick tonal adjustments
- Apply special color effects to images
- Enhance your image with color balance adjustments
- High dynamic range images
- View histograms and pixel values
- Match colors in your image
- Crop and straighten photos
- Convert a color image to black and white
- Adjustment and fill layers
- Curves adjustment
- Blending modes
- Target images for press
- Adjust color and tone with Levels and Curves eyedroppers
- Adjust HDR exposure and toning
- Dodge or burn image areas
- Make selective color adjustments
- Image repair and restoration
- Image enhancement and transformation
- Drawing and painting
- Paint symmetrical patterns
- Draw rectangles and modify stroke options
- About drawing
- Draw and edit shapes
- Create star or any other pointed shape
- Painting tools
- Create and modify brushes
- Blending modes
- Add color to paths
- Edit paths
- Paint with the Mixer Brush
- Brush presets
- Gradients
- Gradient interpolation
- Fill and stroke selections, layers, and paths
- Draw with the Pen tools
- Create patterns
- Generate a pattern using the Pattern Maker
- Manage paths
- Manage pattern libraries and presets
- Draw or paint with a graphics tablet
- Create textured brushes
- Add dynamic elements to brushes
- Gradient
- Paint stylized strokes with the Art History Brush
- Paint with a pattern
- Sync presets on multiple devices
- Migrate presets, actions, and settings
- Text
- Filters and effects
- Saving and exporting
- Color Management
- Web, screen, and app design
- Video and animation
- Printing
- Automation
- Troubleshooting
Format paragraphs
For point type, each line is a separate paragraph. For paragraph type, each paragraph can have multiple lines, depending on the dimensions of the bounding box.
You can select paragraphs and then use the Paragraph panel to set formatting options for a single paragraph, multiple paragraphs, or all paragraphs in a type layer.
-
Select the Horizontal Type tool
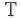 or
the Vertical Type tool
or
the Vertical Type tool 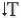 .
.
- To apply formatting to a single paragraph, click in a paragraph.
- To apply formatting to multiple paragraphs, make a selection within a range of paragraphs.
- To apply formatting to all paragraphs in the layer, select the type layer in the Layers panel.
Paragraph panel overview
You
use the Paragraph panel to change the formatting of columns and paragraphs.
To display the panel, choose Window > Paragraph, or
click the Paragraph panel tab if the panel is visible but not active.
You can also select a type tool and click the Panel button ![]() in
the options bar.
in
the options bar.
To set options with numeric values in the Paragraph panel, you can use the up and down arrows or edit the value directly in the text box. When you edit a value directly, press Enter or Return to apply a value, Shift+Enter or Shift+Return to apply a value and then highlight the value just edited, or Tab to apply a value and move to the next text box in the panel.

A. Alignment and justification B. Left indent C. First line left indent D. Space before paragraph E. Hyphenation F. Right indent G. Space after paragraph

You can access additional commands and options in the Paragraph panel menu. To use this menu, click the triangle in the upper-right corner of the panel.
Specify alignment
You can align type to one edge of a paragraph (left, center, or right for horizontal type; top, center, or bottom for vertical type). Alignment options are available only for paragraph type.
-
Do one of the following:
- Select a type layer if you want all the paragraphs in that type layer to be affected.
- Select the paragraphs you want affected.
-
In the Paragraph panel or options bar, click an alignment option.
The options for horizontal type are:
Left Align Text
Aligns type to the left, leaving the right edge of the paragraph ragged.
Center Text
Aligns type to the center, leaving both edges of the paragraph ragged.
Right Align Text
Aligns type to right, leaving the left edge of the paragraph ragged.
The options for vertical type are:
Top Align Text
Aligns type to the top, leaving the bottom edge of the paragraph ragged.
Center Text
Aligns type to the center, leaving both the top and bottom edges of the paragraph ragged.
Bottom Align Text
Aligns type to the bottom, leaving the top edge of the paragraph ragged.
Specify justification for paragraph type
Text is said to be justified when it is aligned with both edges. You can choose to justify all text in a paragraph excluding the last line, or you can justify text in a paragraph including the last line. The settings you choose for justification affect the horizontal spacing of lines and the aesthetic appeal of type on a page.
Justification options are available only for paragraph type and determine word, letter, and glyph spacing. Justification settings apply only to Roman characters; double‑byte characters available in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean fonts are not affected by these settings.
-
Do one of the following:
- Select a type layer if you want all the paragraphs in that type layer to be affected.
- Select the paragraphs you want affected.
-
In the Paragraph panel, click a justification option.
The options for horizontal type are:
Justify Last Left
Justifies all lines except the last, which is left aligned.
Justify Last Centered
Justifies all lines except the last, which is center aligned.
Justify Last Right
Justifies all lines except the last, which is right aligned.
Justify All
Justifies all lines including the last, which is force justified.
The options for vertical type are:
Justify Last Top
Justifies all lines except the last, which is top aligned.
Justify Last Centered
Justifies all lines except the last, which is center aligned.
Justify Last Bottom
Justifies all lines except the last, which is bottom justified.
Justify All
Justifies all lines including the last, which is force justified.
NoteJustification (right, center, and left align, and justify all) for type on a path starts at the insertion point and ends at the end of the path.
Adjust word and letter spacing in justified text
You can precisely control how Photoshop spaces letters and words and scales characters. Adjusting spacing is especially useful with justified type, although you can also adjust spacing for unjustified type.
-
Select the paragraphs you want affected, or select a type layer if you want all the paragraphs in that type layer to be affected.
-
Choose Justification from the Paragraph panel menu.
-
Enter values for Word Spacing, Letter Spacing, and Glyph Scaling. The Minimum and Maximum values define a range of acceptable spacing for justified paragraphs only. The Desired value defines the desired spacing for both justified and unjustified paragraphs:
Word Spacing
The space between words that results from pressing the spacebar. Word Spacing values can range from 0% to 1000%; at 100%, no additional space is added between words.
Letter Spacing
The distance between letters, including kerning or tracking values. Letter Spacing values can range from –100% to 500%; at 0%, no space is added between letters; at 100% , an entire space width is added between letters.
Glyph Scaling
The width of characters (a glyph is any font character). Values can range from 50% to 200%; at 100%, the height of characters is not scaled.
NoteSpacing options are always applied to an entire paragraph. To adjust the spacing in a few characters, but not an entire paragraph, use the Tracking option.
Indent paragraphs
Indention specifies the amount of space between type and the bounding box or line that contains the type. Indention affects only the selected paragraph or paragraphs, so you can easily set different indentions for paragraphs.
-
Do one of the following:
- Select a type layer if you want all the paragraphs in that type layer to be affected.
- Select the paragraphs you want affected.
-
In the Paragraph panel, enter a value for an indention option:
Indent Left Margin
Indents from the left edge of the paragraph. For vertical type, this option controls the indention from the top of the paragraph.
Indent Right Margin
Indents from the right edge of the paragraph. For vertical type, this option controls the indention from the bottom of the paragraph.
Indent First Line
Indents the first line of type in the paragraph. For horizontal type, the first line indent is relative to the left indent; for vertical type, the first line indent is relative to the top indent. To create a first line hanging indent, enter a negative value.
Adjust paragraph spacing
-
Select the paragraphs you want affected, or select a type layer if you want all the paragraphs in that type layer to be affected. If you don’t insert the cursor in a paragraph or select a type layer, the setting applies to new text you create.
-
In the Paragraph panel, adjust the values for Add Space Before Paragraph
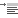 and
Add Space After Paragraph
and
Add Space After Paragraph 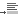 .
.
Specify hanging punctuation for Roman fonts
Hanging punctuation controls the alignment of punctuation marks for a specific paragraph. When Roman Hanging Punctuation is turned on, the following characters appear outside the margins: single quotes, double quotes, apostrophes, commas, periods, hyphens, em dashes, en dashes, colons, and semicolons. When a punctuation character is followed a quotation mark, both characters hang.
Keep in mind that the paragraph alignment determines the margin from which the punctuation hangs. For left-aligned and right-aligned paragraphs, punctuation hangs off the left and right margin, respectively. For top-aligned and bottom-aligned paragraphs, punctuation hangs off the top and bottom margin, respectively. For centered and justified paragraphs, punctuation hangs off both margins.


-
Do one of the following:
- Select a type layer if you want all the paragraphs in that type layer to be affected.
- Select the paragraphs you want affected.
-
Choose Roman Hanging Punctuation from the Paragraph panel menu. A check mark indicates that the option is selected.Note
Double‑byte punctuation marks available in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean fonts in the selected range will not hang when you use Roman Hanging Punctuation. Instead, use either Burasagari Standard or Burasagari Strong. These items are available only if you select Show Asian Text Options in the Type preferences.
Adjust hyphenation automatically
The settings you choose for hyphenation affect the horizontal spacing of lines and the aesthetic appeal of type on a page. Hyphenation options determine whether words can be hyphenated and, if so, what breaks are allowable.
-
To use automatic hyphenation, do any of the following:
- To turn automatic hyphenation on or off, select or deselect the Hyphenate option in the Paragraph panel.
- To apply hyphenation to specific paragraphs, first select only the paragraphs that you want to affect.
- To choose a hyphenation dictionary, choose a language from the Language menu at the bottom of the Character panel.
-
To specify options, choose Hyphenation from the Paragraph panel menu, and specify the following options:
Words Longer Than _ Letters
Specifies the minimum number of characters for hyphenated words.
After First _ Letters And Before Last _ Letters
Specifies the minimum number of characters at the beginning or end of a word that can be broken by a hyphen. For example, by specifying 3 for these values, aromatic would be hyphenated as aro‑ matic instead of ar‑ omatic or aromat‑ ic.
Hyphen Limit
Specifies the maximum number of consecutive lines on which hyphenation may occur.
Hyphenation Zone
Specifies a distance from the right edge of a paragraph, demarcating a portion of the line where hyphenation is not allowed. A setting of 0 allows all hyphenation. This option applies only when you use the Adobe Single‑line Composer.
Hyphenate Capitalized Words
Deselect to prevent capitalized words from being hyphenated.
Hyphenation settings apply only to Roman characters; double‑byte characters available in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean fonts are not affected by these settings.
Prevent words from breaking
You can prevent words from breaking at the end of lines—for example, proper names or words that could be misread when hyphenated. You can also keep multiple words or groups of words together—for example, clusters of initials and a last name.
-
Select the characters you want to prevent from breaking.
-
Choose No Break from the Character panel menu.Note
If you apply the No Break option to too many adjacent characters, the text may wrap in the middle of a word. However, if you apply the No Break option to more than a single line of text, none of the text will appear.
Composition methods
The appearance of type on the page depends on a complex interaction of processes called composition. Using the word spacing, letterspacing, glyph spacing, and hyphenation options you’ve selected, Adobe applications evaluate possible line breaks and choose the one that best supports the specified parameters.
You can choose between two composition methods: the Adobe Every‑line Composer and the Adobe Single‑line Composer. Both methods evaluate possible breaks and choose the one that best supports the hyphenation and justification options you’ve specified for a given paragraph. The composition method affects only the selected paragraph or paragraphs, so you can easily set different composition methods for different paragraphs.
Every‑line Composer
The Every‑line Composer considers a network of break points for a range of lines and thus can optimize earlier lines in the paragraph in order to eliminate especially unattractive breaks later on.
The Every‑line Composer approaches composition by identifying possible break points, evaluating them, and assigning a weighted penalty based on the following principles:
For left-, right-, or center-aligned text, lines that fall closer to the right side are favored and have a lower penalty.
For justified text, the highest importance is given to evenness of letter and word spacing.
Hyphenation is avoided when possible.
Single-line Composer
The Single-line composer offers a traditional approach to composing type one line at a time. This option is useful if you want manual control over how lines break. The Single‑line Composer uses the following principles when considering a breakpoint:
Longer lines are favored over shorter lines.
In justified text, compressed or expanded word spacing is preferable to hyphenation.
In nonjustified text, hyphenation is preferable to compressed or expanded letterspacing.
If spacing must be adjusted, compression is better than expansion.
To choose one of these methods, select it from the Paragraph panel menu. To apply the method to all paragraphs, first select the type object; to apply the method to the current paragraph only, first insert the cursor in that paragraph.
Paragraph styles
A paragraph style includes both character and paragraph formatting attributes, and can be applied to a paragraph or range of paragraphs. You can create Paragraph styles and then apply them later.
Choose Window > Paragraph Styles to open the Paragraph Styles panel. By default, each new document contains a Basic Paragraph style that is applied to text you type. You can edit this style, but you can’t rename or delete it. You can rename and delete styles that you create. You can also select a different default style to apply to text.
- To apply a paragraph style, select the text or text layer and click a paragraph style.
Type styles are hierarchical: Manual overrides supersede any applied character styles, which in turn replace applied paragraph styles. This hierarchical approach lets you combine the efficiency of styles with the flexibility to customize your designs.
For a video overview, see Paragraph and Character Styles in Photoshop CS6 by Julieanne Kost.
(Creative Cloud only) You can specify character and paragraph styles as default types styles. For more information see Specifying default type styles | Creative Cloud only.
Create a paragraph style
- If you want to base a new style on the formatting of existing text, select that text or place the insertion point in it.
- Choose New Paragraph Style from the Paragraph Styles panel menu.
Note:To create a style without first selecting text, click the Create New Style icon ![]() at the bottom of the Paragraph Styles panel. To edit a style without applying it to text, select an image layer, such as the Background.
at the bottom of the Paragraph Styles panel. To edit a style without applying it to text, select an image layer, such as the Background.
Edit a paragraph style
Double-click existing styles to edit them and update all associated text in the current document. When you change the formatting of a style, all text to which the style has been applied will be updated with the new format.
To edit a paragraph style, do the following:
- Double-click the style in the Paragraph style panel.
- To specify the formatting attributes, click a category (such as Basic Character Formats) on the left, and specify the attributes to add to the style.
When specifying a Character Color in the Style Options dialog box, you can create a new color by double-clicking the fill or stroke box.
- When you’ve finished specifying the formatting attributes, click OK.