- Substance 3D home
- Home
- Getting Started
- Interface
- Objects
- Using Stager
- Features
- Common issues
- Release notes
Material projections
To change projection modes
- Select a material
- In the Properties panel set the Projection to the style you want to use


UV projection
UV workflows work by cutting seams into the 3D model and flattening the model out into a 2D space (called UVW coordinates, or UVs for short). The material textures are projected onto the flattened UVs which act as a map between the 2D image and the 3D surface of the model.
UV based workflows can be best when you want to have precise control over seams or want localized texture details in specific areas of a model (such as a decal or label). Creating UVs can be done with automatic processes (such as Stager’s option found under the menu Object > Generate UVs) or via manual tools in 3D modeling applications.


UV projection options
Repeat
Sets the number of times all material textures should repeat in UV space. If your textures were designed for the specific model (such as with a texturing tool like Substance 3D Painter) then this should remain set to a 1 by 1 repeat.


Offset
Transforms all material textures in UV space by offsetting its position or rotation.


Limitations for UV projection workflows
UV layouts can be time consuming to create. Manual UV creation requires creating seams, flattening the pieces, and organizing the pieces. Many modeling and creation tools have advanced toolsets for this and it's an entire discipline for modeling and texturing artists. Automatic UV unwrapping can create fast results, but often with unwanted seam placement or high levels of distortion.
Another limitation is that the scale of the material is controlled by the UV itself. For example, the pillows on this couch are using the same material, but because the UVs are created differently the material on the pillows appears at different scales.


Triplanar projection
Triplanar projection is a method that does not rely on the object having UVs at all. The material is instead projected onto the surface of the model from three planes (X, Y, and Z axis). Seams will show wherever the 'planes' of the projection meet but can be blended together in real time (unlike UV seams, which cannot blend).
Triplanar workflows can be faster and easier when you want to use materials without having to spend time on UV generation and when precise seams or localized texture details are not necessary. Triplanar is best suited for seamless, repeating textures with noise, such as wood, metal, rock, plaster.
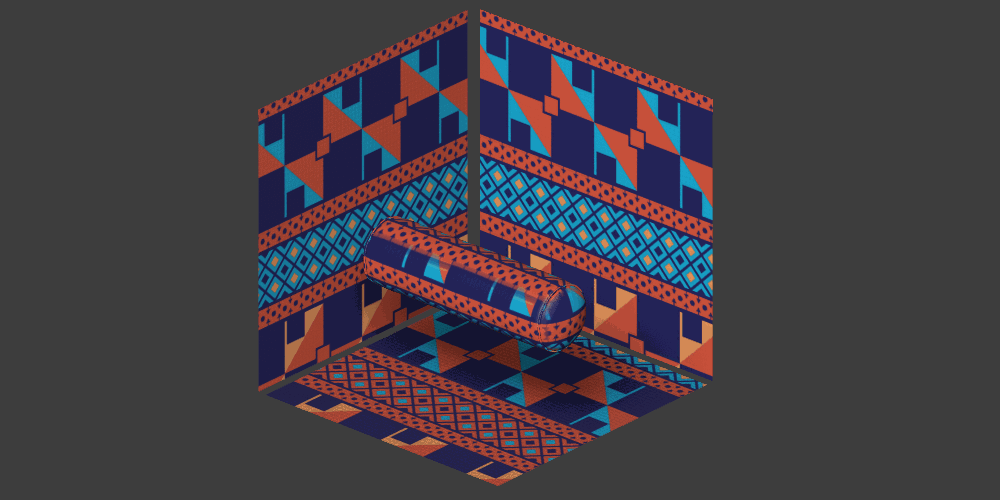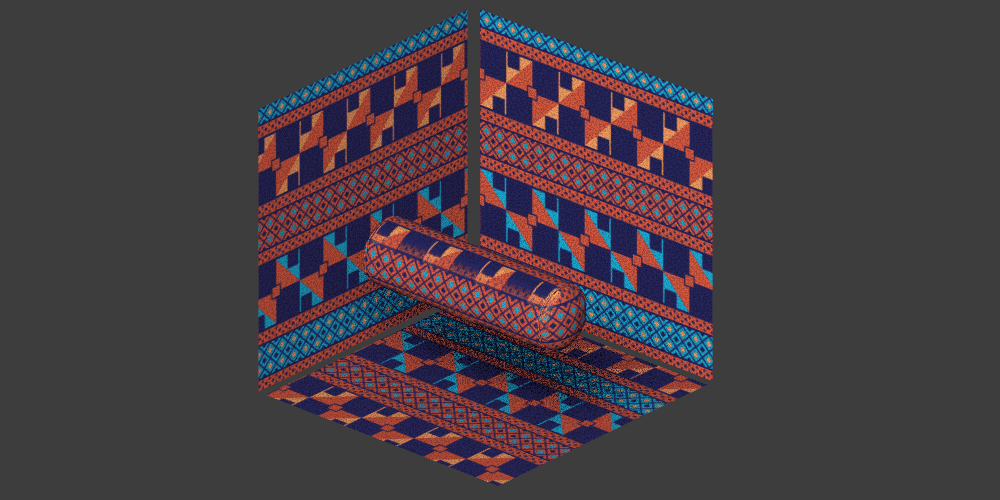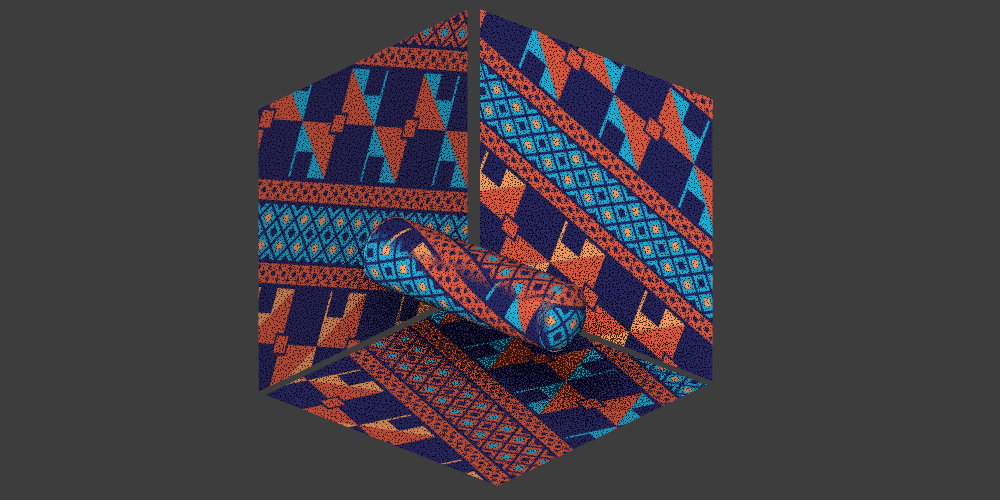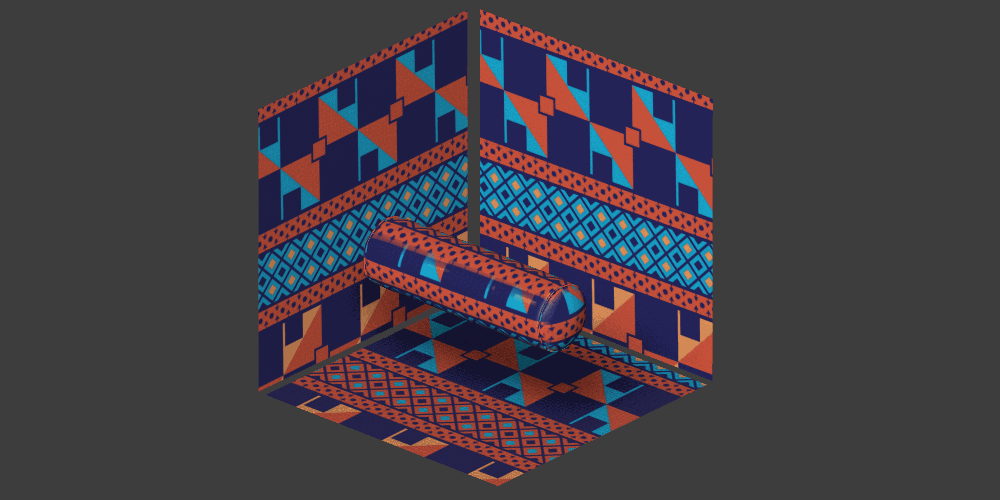

Triplanar projection options
Local mode
Triplanar (local) means that the triplanar projection is aligned ‘locally’ to each object. The result is that the material will follow the object's position, rotation, and scale.
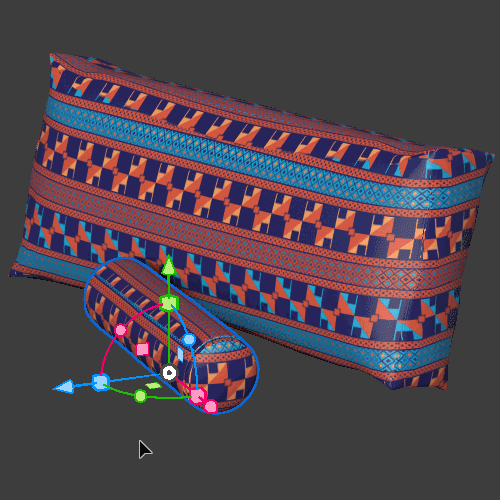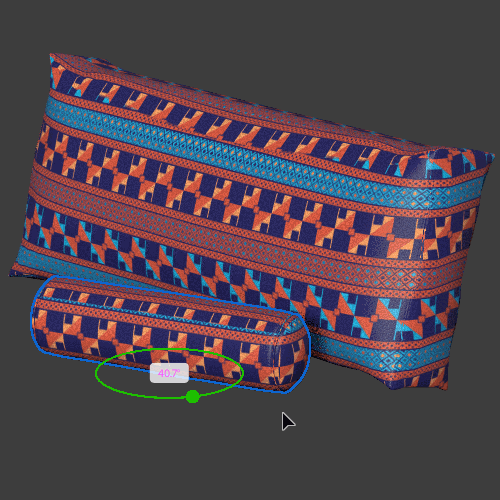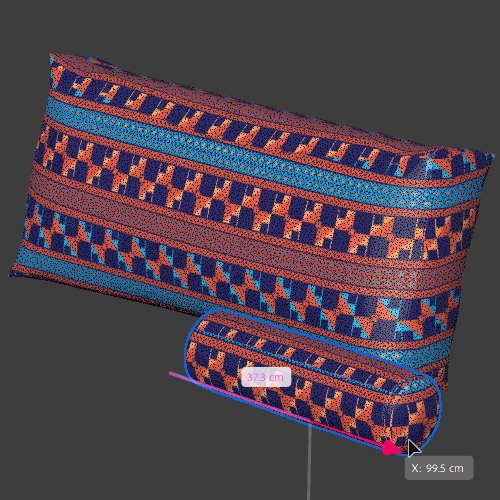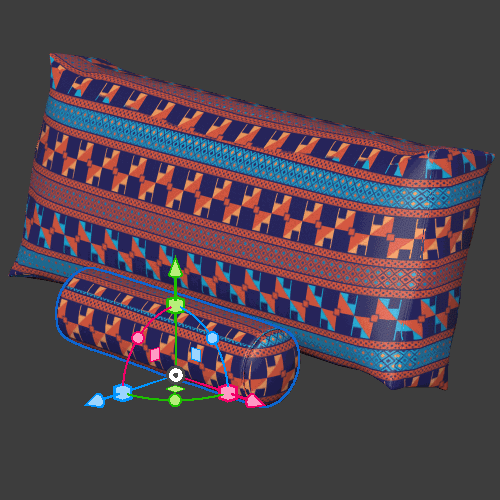

Global mode
Triplanar (global) means that the projection is aligned ‘globally’ to the X, Y, Z coordinates of the scene. The result is that the material will give different results based on the position and rotation of the objects and will not follow them if they are moved.


Scale: Custom Repeat
Custom repeat: Only available while using triplanar (local). Repeat the material across the bounding box of the object. A repeat of 1 will repeat the material one time across the objects bounding box. Objects of different sizes will display the material at different visual scales based on their own bounding box size.


Scale: Physical size
Available for local and global. Repeats the material by setting a physical unit for the projection. The material will repeat infinitely, and the visual size will be consistent across all objects. Physical size is only accurate if the object is modeled to scale. If its scale is changed in local mode, the material will also scale with it. Modeling to real world units and keeping the Stager scale factor to 1 is best practice for accurate physical size workflows.


Offset
Transforms all material textures by offsetting the projection position or rotation.
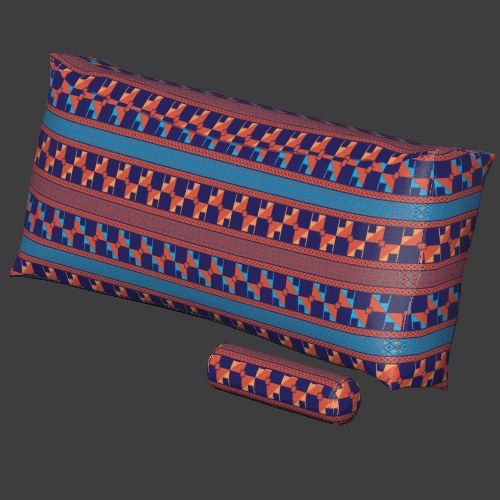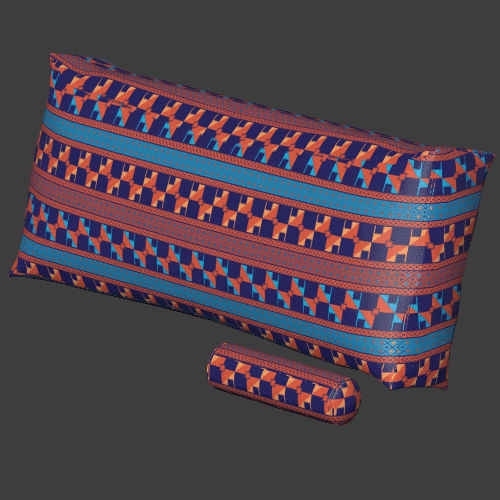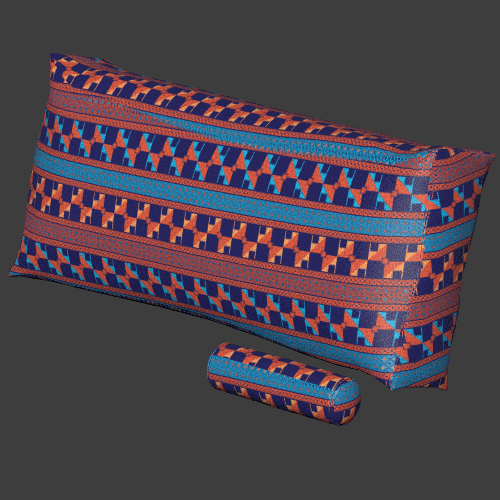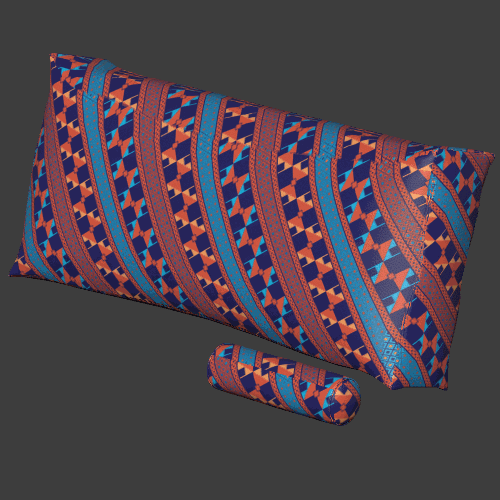

Seam blending
Blends the textures between the three planar projections to make the seams sharper or blurrier.
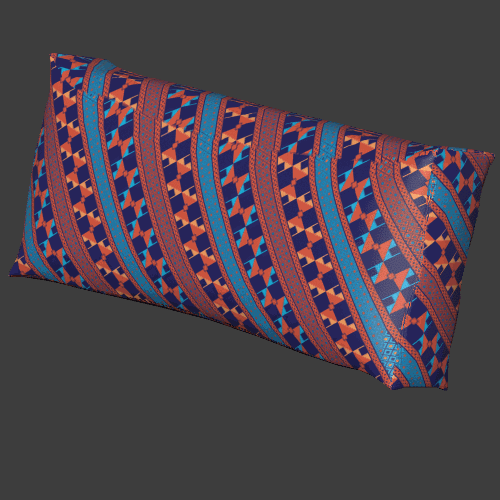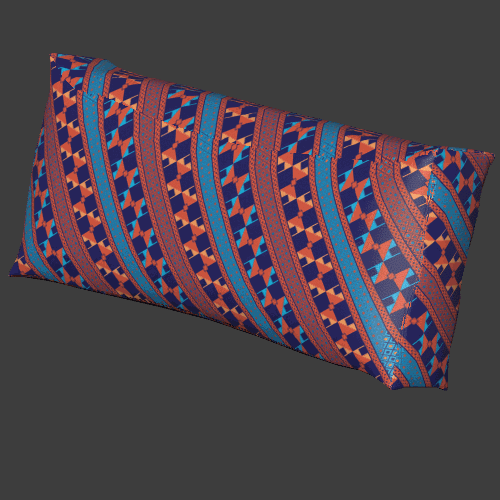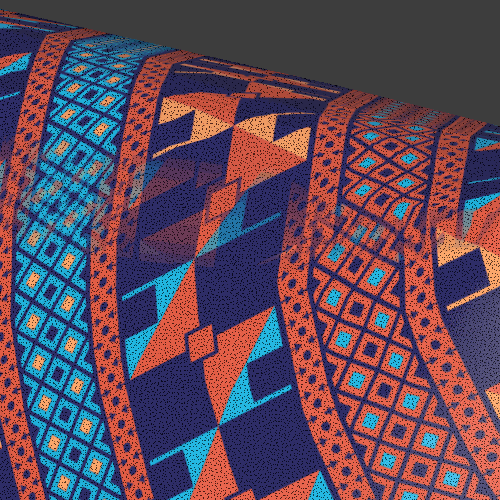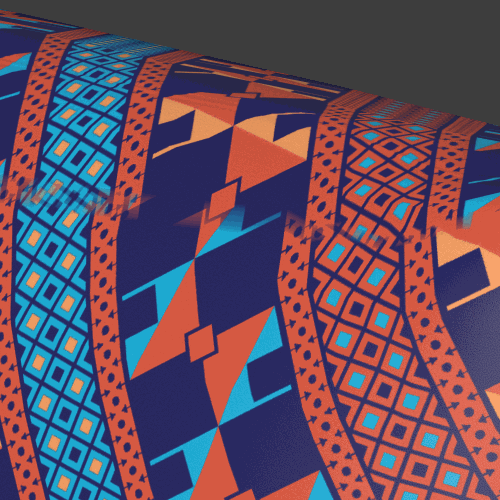

Limitations for triplanar workflows
Triplanar works best for materials with natural noise and variation like rocks, wood, metal, plastics, papers. Patterns and lines that need to precisely match can give varying results depending on the object.
Triplanar works with displacement but will not work in the unique combination of using instanced meshes with displacement enabled and the material set to triplanar in global mode. This is because the displacement in global mode would generate a unique mesh, which would make the mesh no longer an instance. In this case the results will be incorrect.
Currently Stager’s decal feature requires the object to have UVs. Applying a decal to an object will force the underlying material into UV application mode so that they can be composited together.

