Documentation for Substance Designer 3D is now available on Experience League. After March 14th, HelpX pages will automatically redirect to the equivalent Experience League page.
Refer to the FAQ for more information about which documentation is affected.
- Substance 3D home
- User guide
- Glossary
- Getting started
- Workspace
- Workspace
- Customizing your workspace
- Home screen
- Main toolbar
- Preferences
- Explorer
- Graph view
- Library
- Properties
- 2D view
- 3D view
- Dependency manager
- Resources
- Resources
- Importing, linking and new resources
- Bitmap resource
- Vector graphics (SVG) resource
- 3D scene resource
- AxF (Appearance eXchange Format)
- Font resource
- Warnings from dependencies
- Substance graphs
- Substance graphs
- Substance graph key concepts
- Creating a Substance graph
- Instances and subgraphs
- Graph parameters
- Manage parameters
- 'Visible if' expressions
- Inheritance in Substance graphs
- Output size
- Values in Substance graphs
- Publishing Substance 3D asset files (SBSAR)
- Exporting bitmaps
- Exporting PSD files
- Sample Substance graphs
- Warnings in Substance graphs
- Nodes reference for Substance graphs
- Nodes reference for Substance graphs
- Atomic nodes
- Node library
- Node library
- Texture generators
- Texture generators
- Noises
- Noises
- 3D Perlin noise
- 3D Perlin noise fractal
- 3D Ridged noise fractal
- 3D Simplex noise
- 3D Voronoi
- 3D Voronoi fractal
- 3D Worley noise
- Anisotropic noise
- Blue noise fast
- BnW spots 1
- BnW spots 2
- BnW spots 3
- Cells 1
- Cells 2
- Cells 3
- Cells 4
- Clouds 1
- Clouds 2
- Clouds 3
- Creased
- Crystal 1
- Crystal 2
- Directional noise 1
- Directional noise 2
- Directional noise 3
- Directional noise 4
- Directional scratches
- Dirt 1
- Dirt 2
- Dirt 3
- Dirt 4
- Dirt 5
- Dirt gradient
- Fluid
- Fractal sum 1
- Fractal sum 2
- Fractal sum 3
- Fractal sum 4
- Fractal sum base
- Fur 1
- Fur 2
- Fur 3
- Gaussian noise
- Gaussian spots 1
- Gaussian spots 2
- Grunge concrete
- Grunge Damas
- Grunge galvanic large
- Grunge galvanic small
- Grunge leaks
- Grunge leaky paint
- Grunge map 001
- Grunge map 002
- Grunge map 003
- Grunge map 004
- Grunge map 005
- Grunge map 006
- Grunge map 007
- Grunge map 008
- Grunge map 009
- Grunge map 010
- Grunge map 011
- Grunge map 012
- Grunge map 013
- Grunge map 014
- Grunge map 015
- Grunge rough dirty
- Grunge rust fine
- Grunge scratches dirty
- Grunge scratches fine
- Grunge scratches rough
- Grunge shavings
- Grunge splashes dusty
- Grunge spots
- Grunge spots dirty
- Liquid
- Messy fibers 1
- Messy fibers 2
- Messy fibers 3
- Microscope view
- Moisture noise 1
- Moisture noise 2
- Perlin noise
- Plasma
- Caustics
- Voronoi
- Voronoi fractal
- Waveform 1
- White noise
- White noise fast
- Patterns
- Patterns
- 3D linear gradient
- 3D volume mask
- Alveolus
- Arc pavement
- Brick 1
- Brick 2
- Brick generator
- Checker 1
- Cube 3D
- Cube 3D GBuffers
- Fibers 1
- Fibers 2
- Gaussian 1
- Gaussian 2
- Gradient axial
- Gradient axial reflected
- Gradient circular
- Gradient linear 1
- Gradient linear 2
- Gradient linear 3
- Gradient radial
- Height extrude
- Mesh 1
- Mesh 2
- Panorama shape
- Polygon 1
- Polygon 2
- Scratches generator
- Shape
- Shape extrude
- Shape mapper
- Shape splatter
- Shape splatter blend
- Shape splatter data extract
- Shape splatter to mask
- Splatter
- Splatter circular
- Star
- Starburst
- Stripes
- Tile generator
- Tile random
- Tile random 2
- Tile sampler
- Triangle grid
- Weave 1
- Weave 2
- Weave generator
- Filters
- Filters
- Adjustments
- Adjustments
- Apply color palette
- Auto levels
- Channel mixer
- Chrominance extract
- Clamp
- Color match
- Color to mask
- Contrast/Luminosity
- Convert to linear
- Convert to sRGB
- Create color palette (16)
- Grayscale conversion advanced
- Hald CLUT
- HDR range viewer
- Height map frequencies mapper
- Highpass
- Histogram compute
- Histogram equalize
- Histogram range
- Histogram render
- Histogram scan
- Non-uniform histogram scan
- Histogram select
- Histogram shift
- ID to mask grayscale
- Invert
- Lighting cancel high frequencies
- Lighting cancel low frequencies
- Luminance highpass
- Min max
- Modify color palette
- Pow
- Quantize color (Simple)
- Quantize color
- Quantize grayscale
- Replace color
- Replace color range
- Threshold
- View color palette
- Blending
- Blurs
- Channels
- Effects
- Effects
- 3D texture position
- 3D texture SDF
- 3D texture surface render
- 3D texture volume render
- Ambient occlusion (HBAO)
- Ambient occlusion (RTAO)
- Anisotropic Kuwahara color
- Anisotropic Kuwahara grayscale
- Bevel
- Bevel smooth
- Cross section
- Curvature
- Curvature smooth
- Curvature sobel
- Diffusion color
- Diffusion grayscale
- Diffusion UV
- Directional distance
- Edge detect
- Emboss with gloss
- Extend shape
- Flood fill
- Flood fill mapper
- Flood fill to Bbox size
- Flood Fill to gradient
- Flood Fill to grayscale/color
- Flood Fill to index
- Flood Fill to position
- Flood Fill to random color
- Flood Fill to random grayscale
- FXAA
- Glow
- Mosaic
- Multi directional warp
- Non-uniform directional warp
- Reaction diffusion fast
- RT irradiance
- RT shadow
- Shadows
- Shape drop shadow
- Shape glow
- Shape stroke
- Summed area table
- Swirl
- Uber emboss
- Vector morph
- Vector warp
- Normal map
- Tiling
- Transforms
- Material filters
- Material filters
- 1-click
- Effects (Material)
- Transforms (Material)
- Blending (Material)
- PBR utilities
- Scan processing
- Mesh-based generators
- Mesh-based generators
- Mask generators
- Weathering
- Utilities (Mesh-based generators)
- Spline & Path tools
- Spline & Path tools
- Working with Path & Spline tools
- Paths to spline
- Path tools
- Spline tools
- Spline tools
- Point list
- Scatter on Spline color
- Scatter on Spline grayscale
- Scatter Splines on Splines
- Spline 2D transform
- Spline (Cubic)
- Spline (Poly quadratic)
- Spline (Quadratic)
- Spline append
- Spline bridge (2 Splines)
- Spline bridge (List)
- Spline bridge mapper color
- Spline bridge mapper grayscale
- Spline circle
- Spline fill
- Spline flow mapper
- Spline mapper color
- Spline mapper grayscale
- Spline merge list
- Spline render
- Spline sample height
- Spline sample thickness
- Spline select
- Spline warp
- UV mapper color
- UV mapper grayscale
- 3D view (Library)
- 3D view (Library)
- HDRI tools
- Node library
- Substance function graphs
- Substance function graphs
- What is a Substance function graph?
- Create and edit a function
- The Substance function graph
- Variables
- FX-maps
- FX-Maps
- How it works
- The Iterate node
- The Quadrant node
- Using Substance function graphs in FX-Maps
- Warnings in Substance function graphs
- Sample Substance function graphs
- Nodes reference for Substance function graphs
- Nodes reference for Substance function graphs
- Function nodes overview
- Atomic function nodes
- Function node library
- MDL graphs
- Working with 3D scenes
- Bakers
- Best practices
- Pipeline and project configuration
- Color management
- Package metadata
- Scripting
- Scripting
- Plugin basics
- Plugin search paths
- Plugins packages
- Plugin manager
- Python editor
- Accessing graphs and selections
- Nodes and properties
- Undo and redo
- Application callbacks
- Creating user interface elements
- Adding actions to the Explorer toolbar
- Using color management
- Using spot colors
- Logging
- Using threads
- Debugging plugins using Visual Studio Code
- Porting previous plugins
- Packaging plugins
- Scripting API reference
- Technical issues
- Release notes


The Node Alignment Tools let you arrange nodes in graphs to improve their readability and authoring experience. They offer actions for aligning nodes, distributing them evenly and snapping them to the grid.
They act on the nodes currently selected only.
Some actions have keyboard shortcuts for quick acces: H, V and S. They are displayed between parentheses in the list of actions below.
Note that these will override any keyboard shortcut assigned to nodes.
In this page
Nodes may be aligned horizontally and vertically, with three modes for each axis:
Horizontal alignments
![]() Left: Align the left side of the selected nodes to the left side of the leftmost node.
Left: Align the left side of the selected nodes to the left side of the leftmost node.
![]() Center (H): Align the horizontal center of the selected nodes to the horizontal center of the bounding box encompassing them.
Center (H): Align the horizontal center of the selected nodes to the horizontal center of the bounding box encompassing them.
![]() Right: Align the right side of the selected nodes to the right side of the rightmost node.
Right: Align the right side of the selected nodes to the right side of the rightmost node.
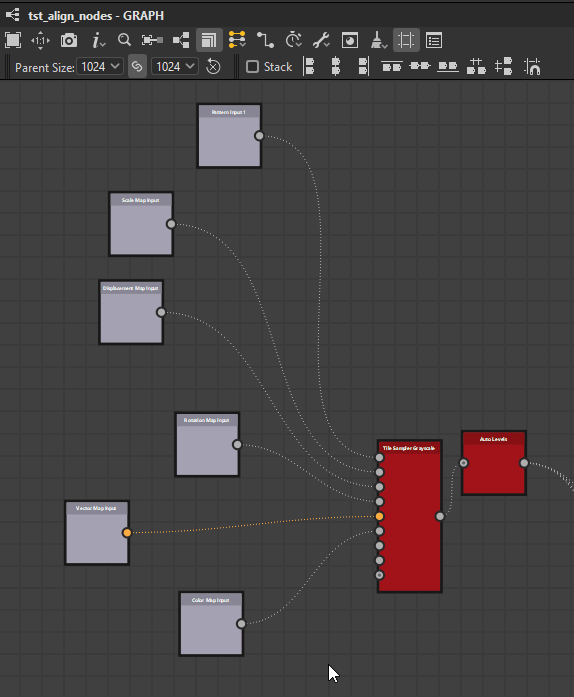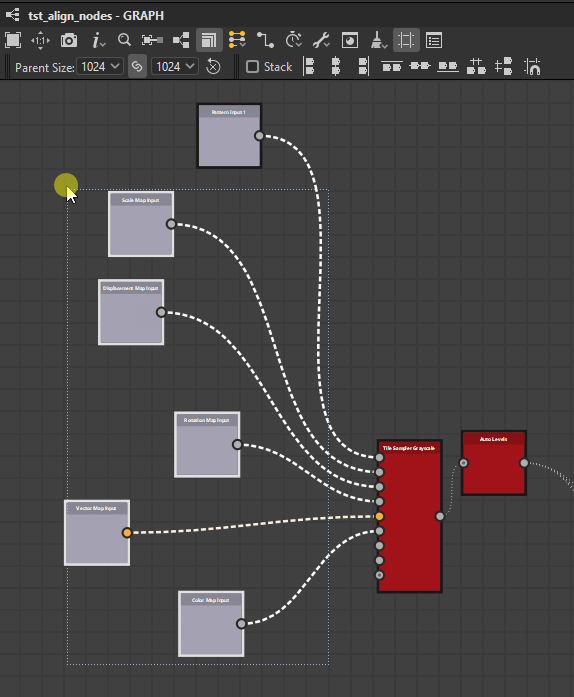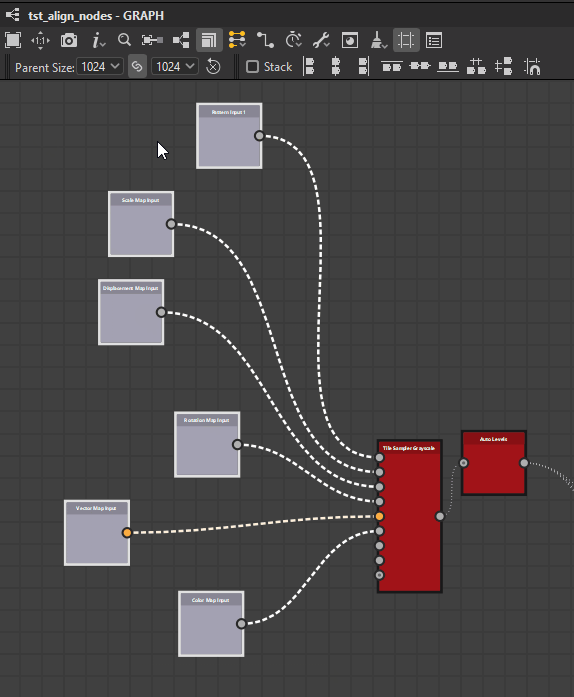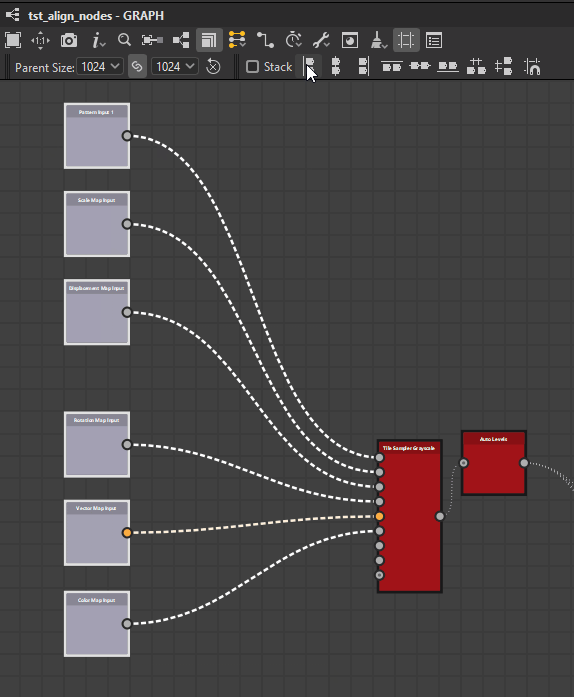

Left
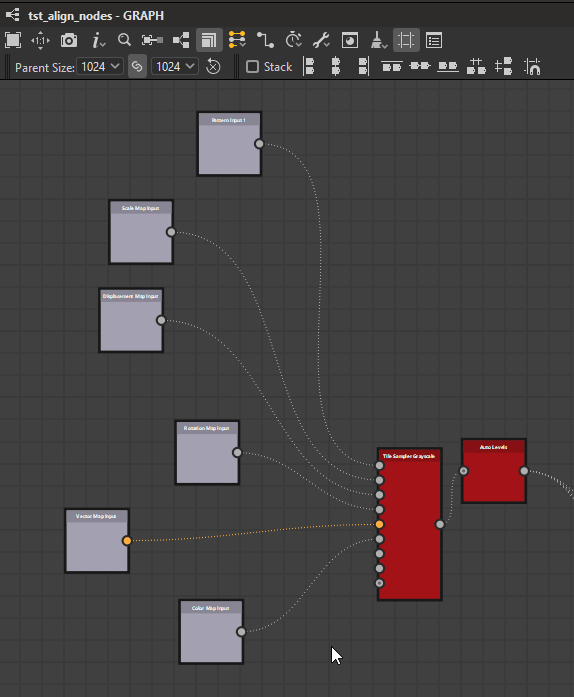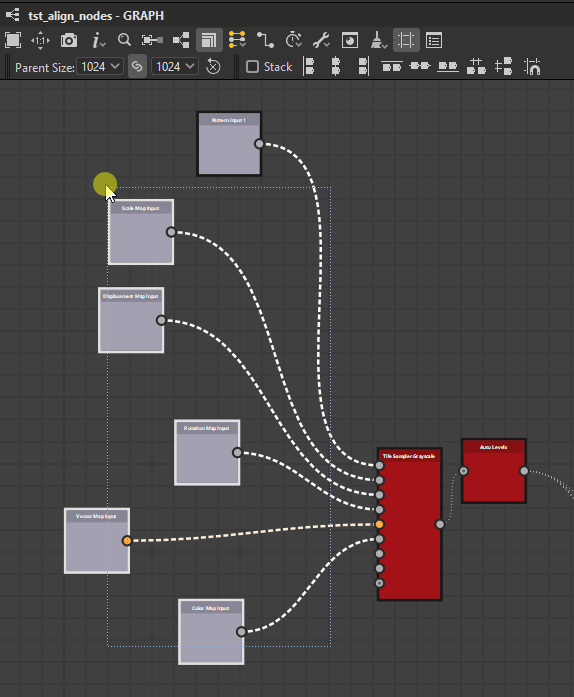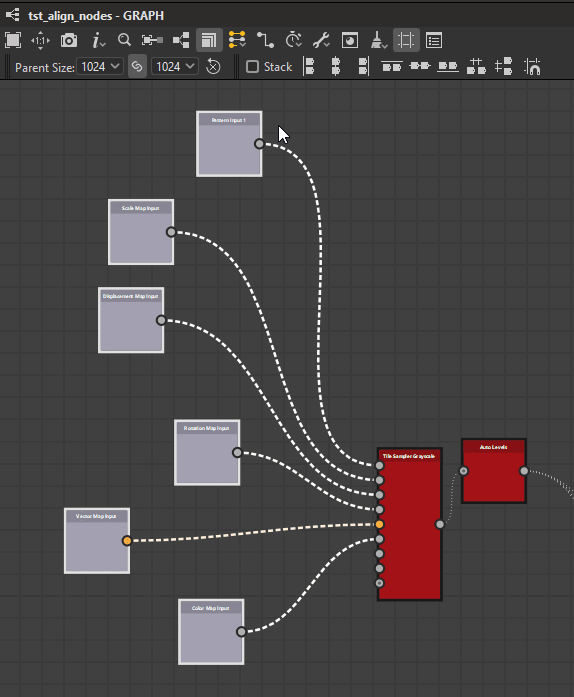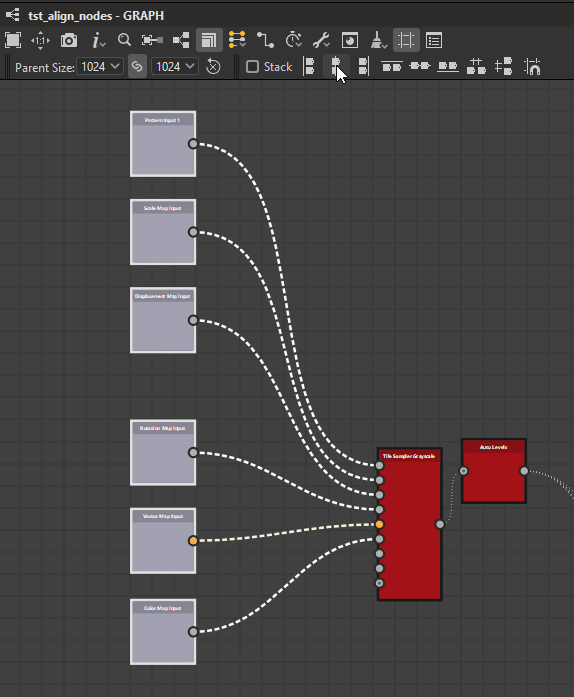

Center
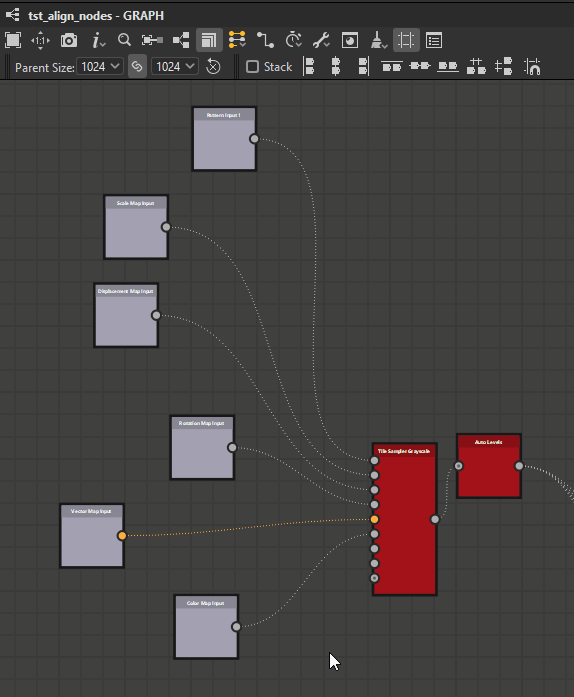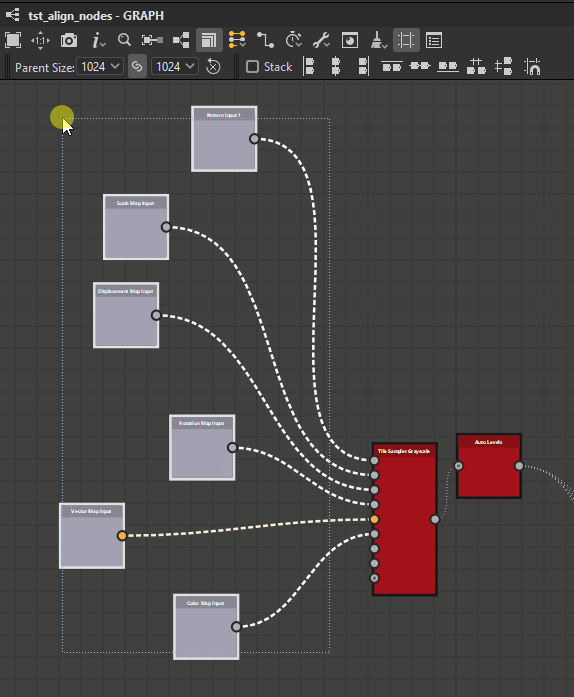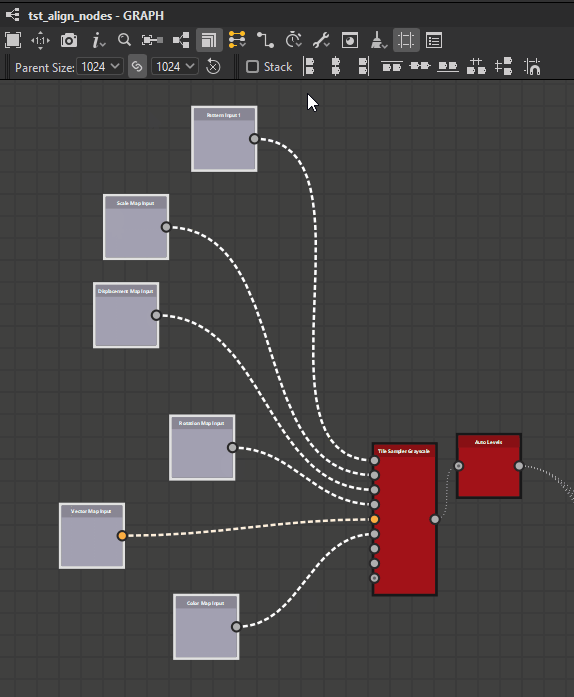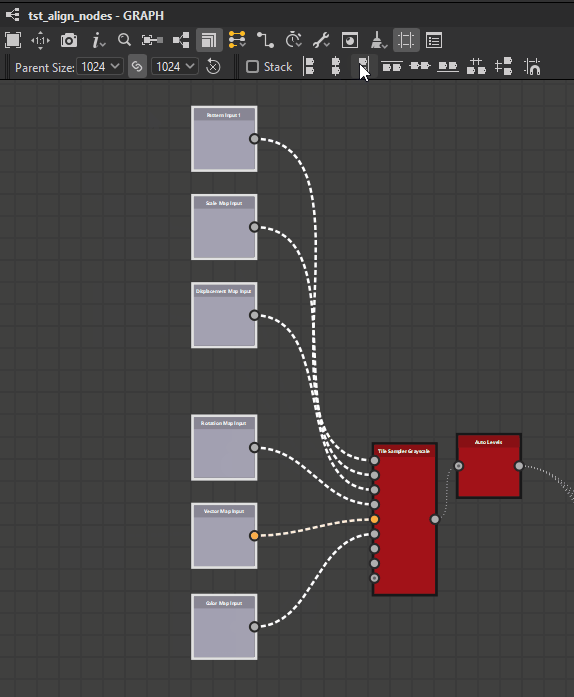

Right
Vertical alignments
![]() Top: Align the top side of the selected nodes to the top side of the uppermost node.
Top: Align the top side of the selected nodes to the top side of the uppermost node.
![]() Middle (V): Align the vertical center of the selected nodes to the vertical center of the bounding box encompassing them.
Middle (V): Align the vertical center of the selected nodes to the vertical center of the bounding box encompassing them.
![]() Bottom: Align the bottom side of the selected nodes to the bottom side of the lowermost node.
Bottom: Align the bottom side of the selected nodes to the bottom side of the lowermost node.
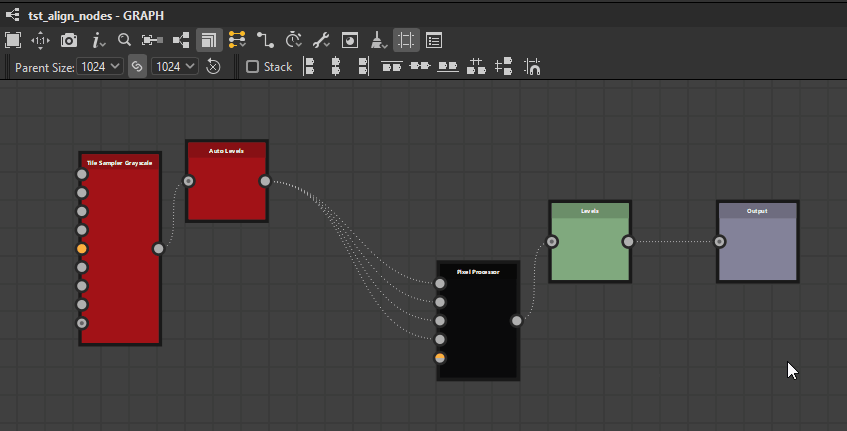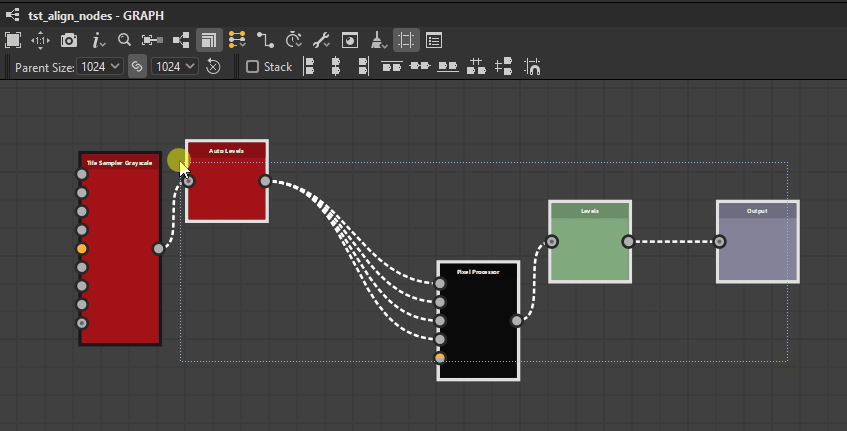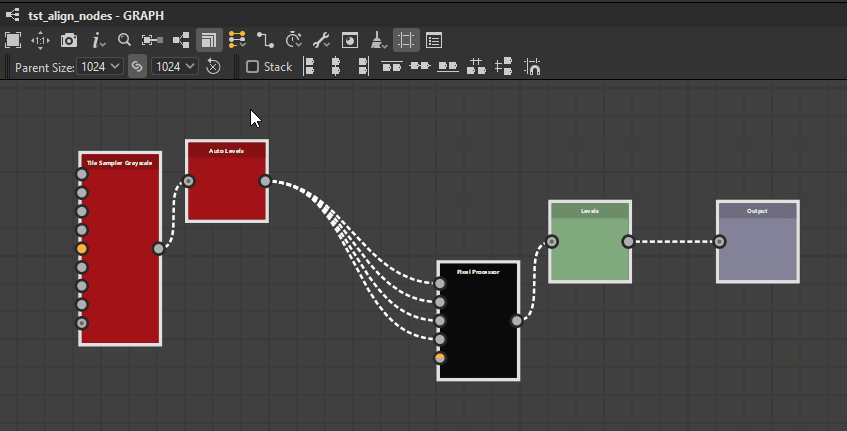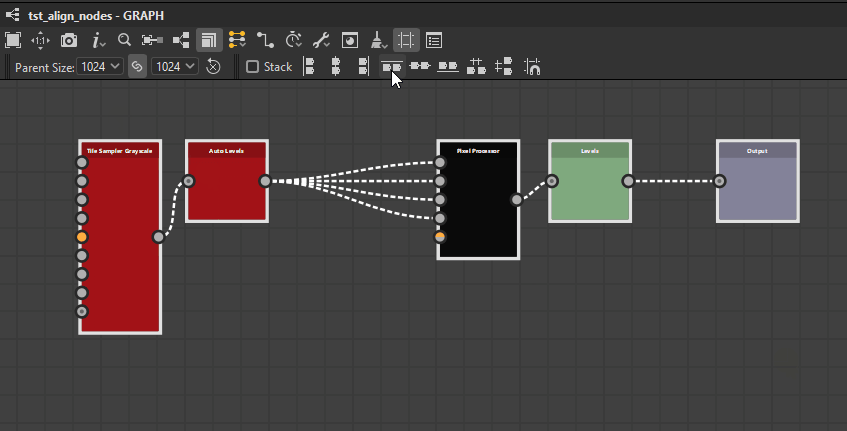

Top
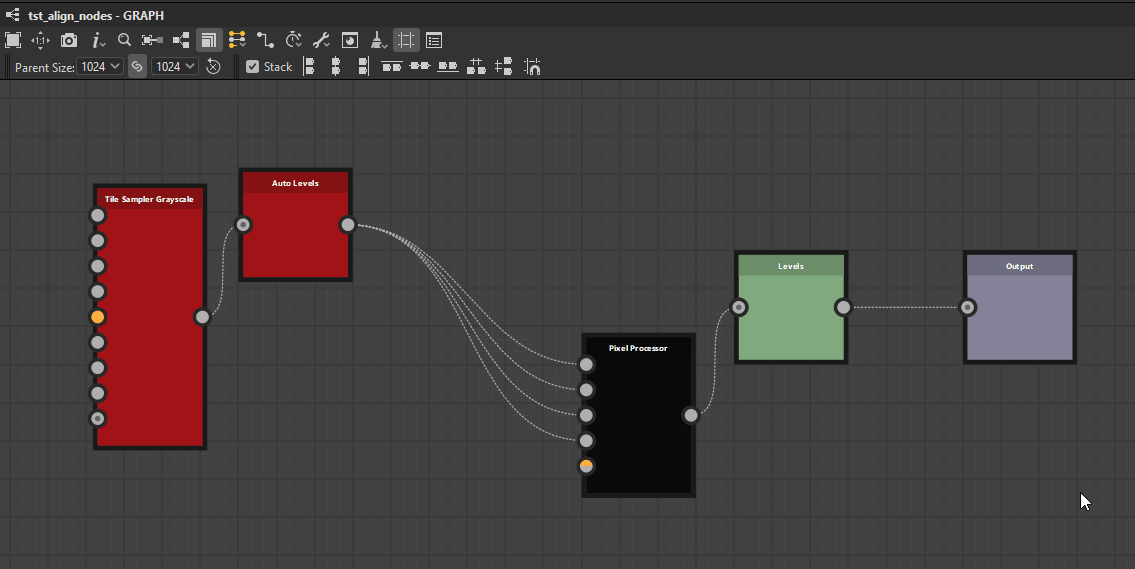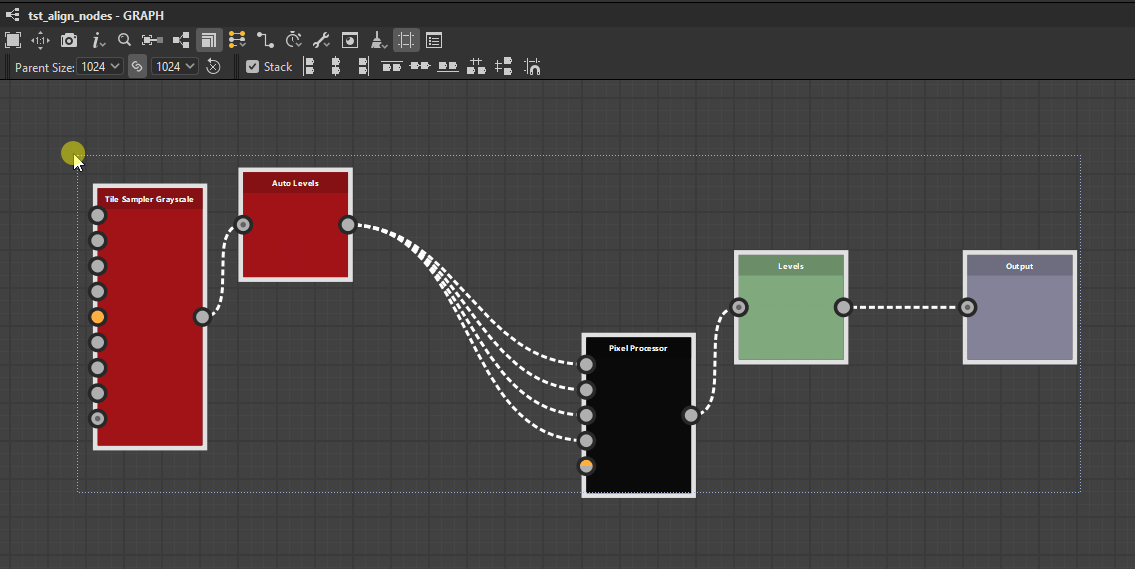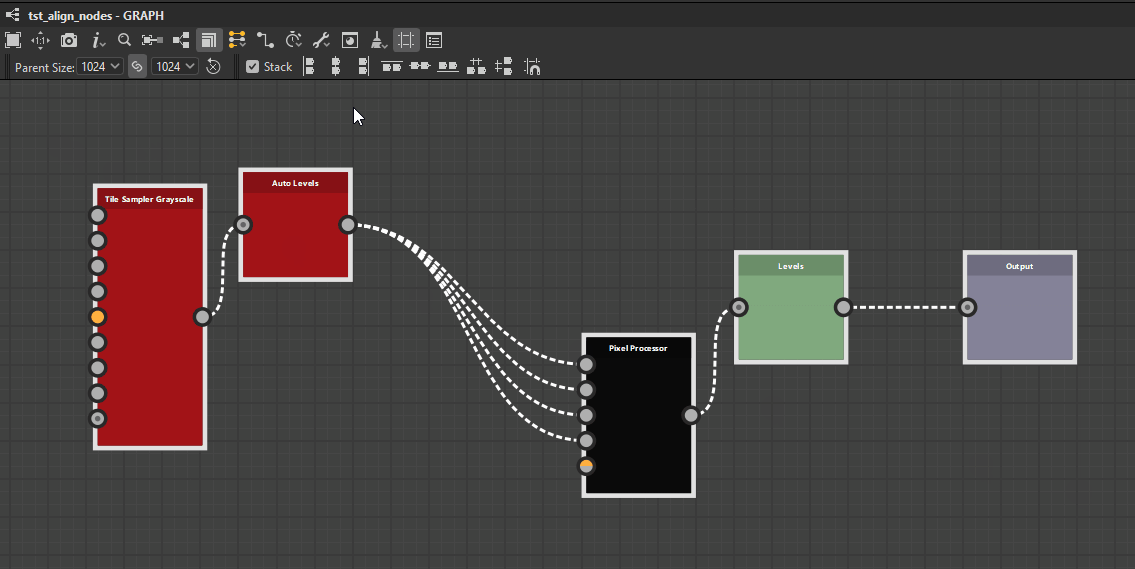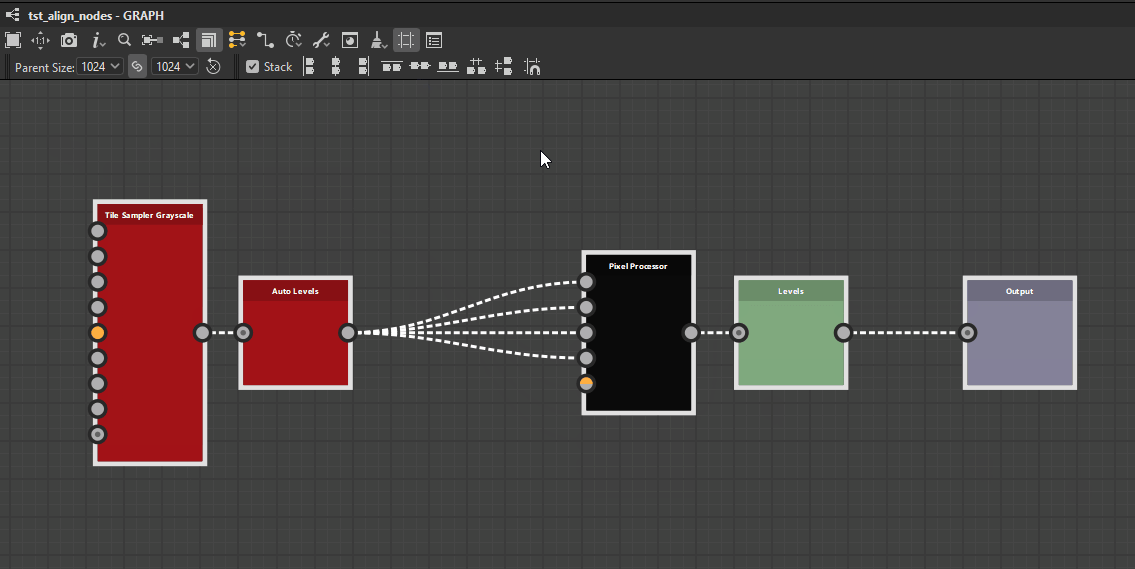

Middle

Bottom
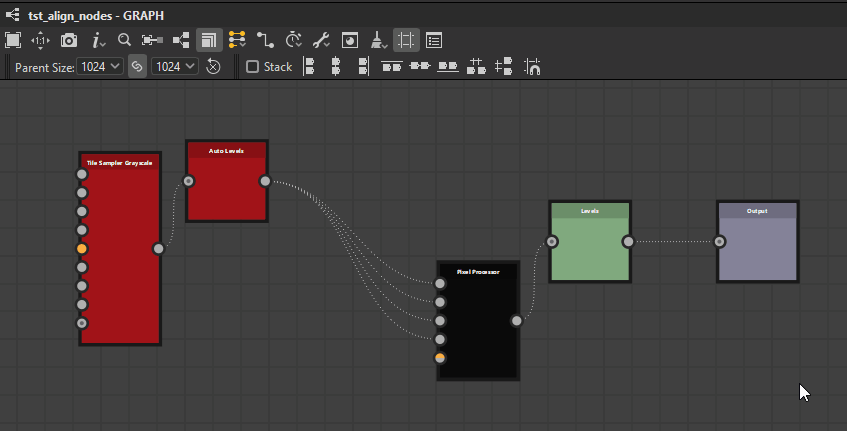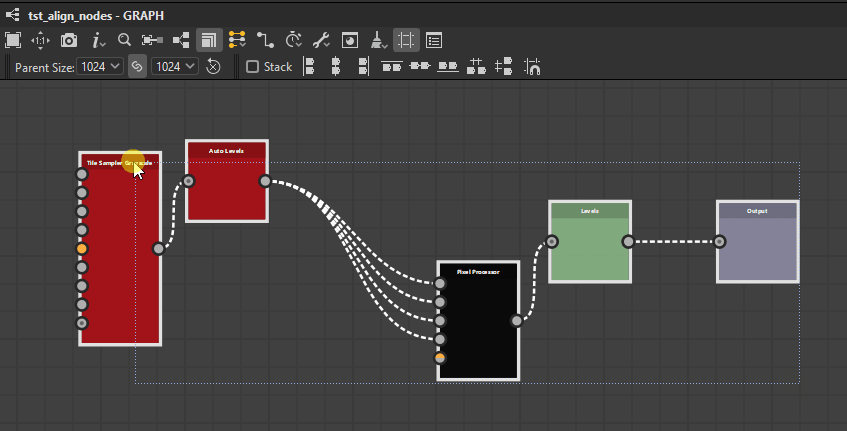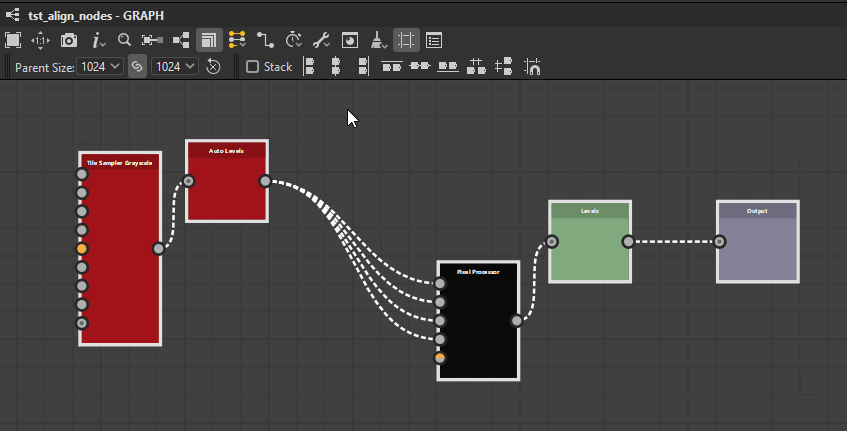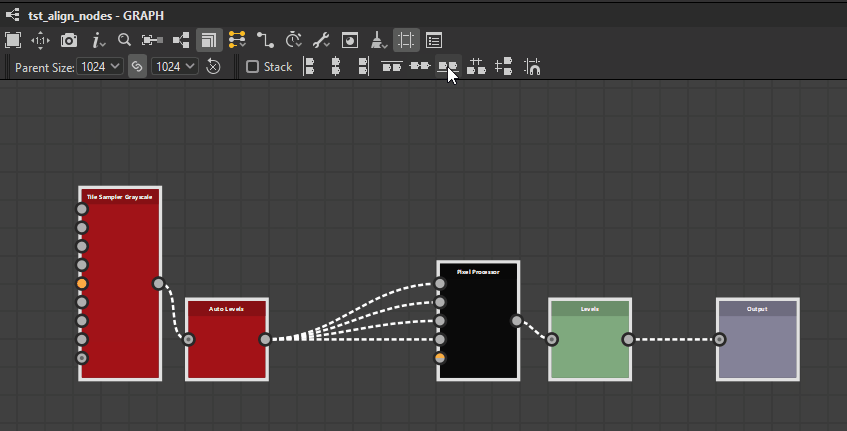
Stacking
The Stack option ![]() lets you avoid any overlap when using alignments. It is enabled by default.
lets you avoid any overlap when using alignments. It is enabled by default.
When enabled, nodes will be moved as far as possible to the reference position until they would collide with another node in the selection. This effectively stacks them in the selected axis with a margin of one medium grid cell between each node.
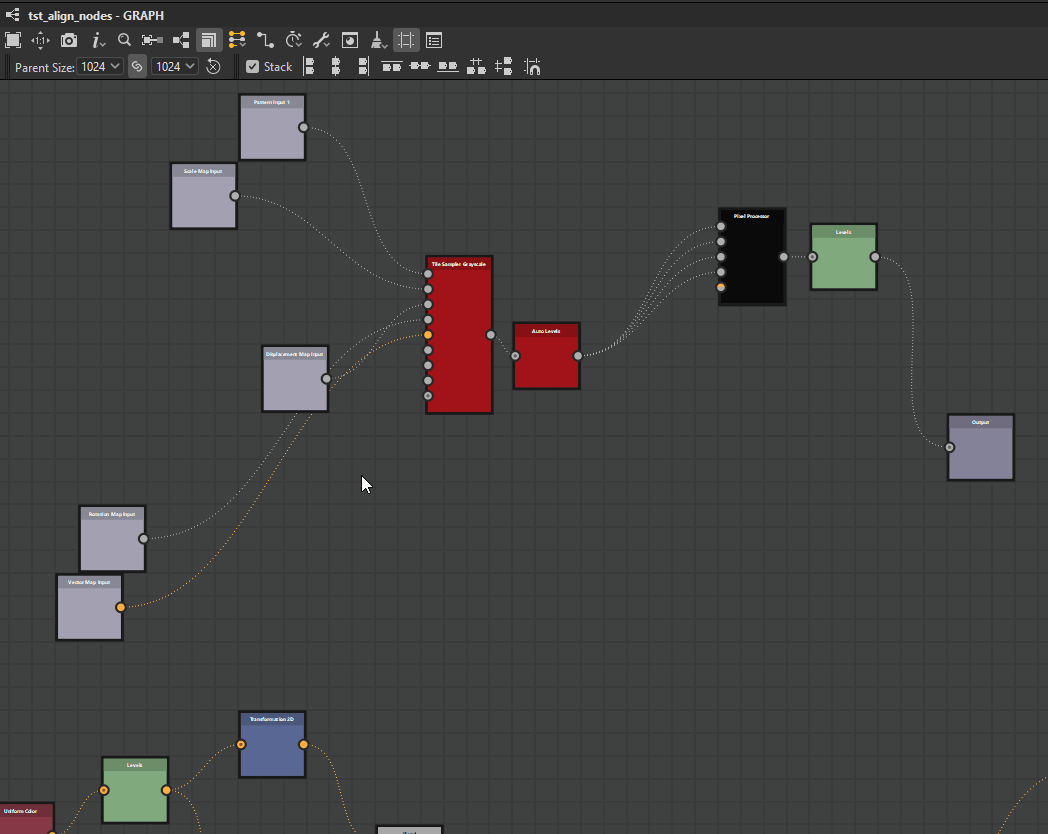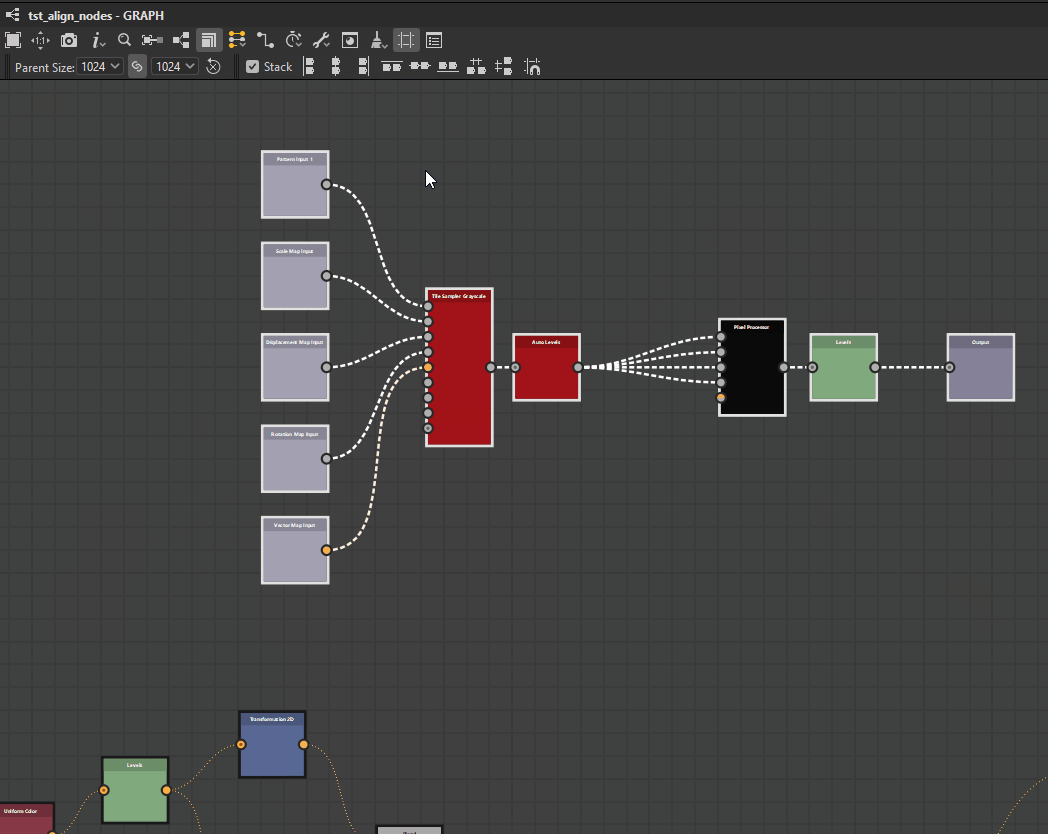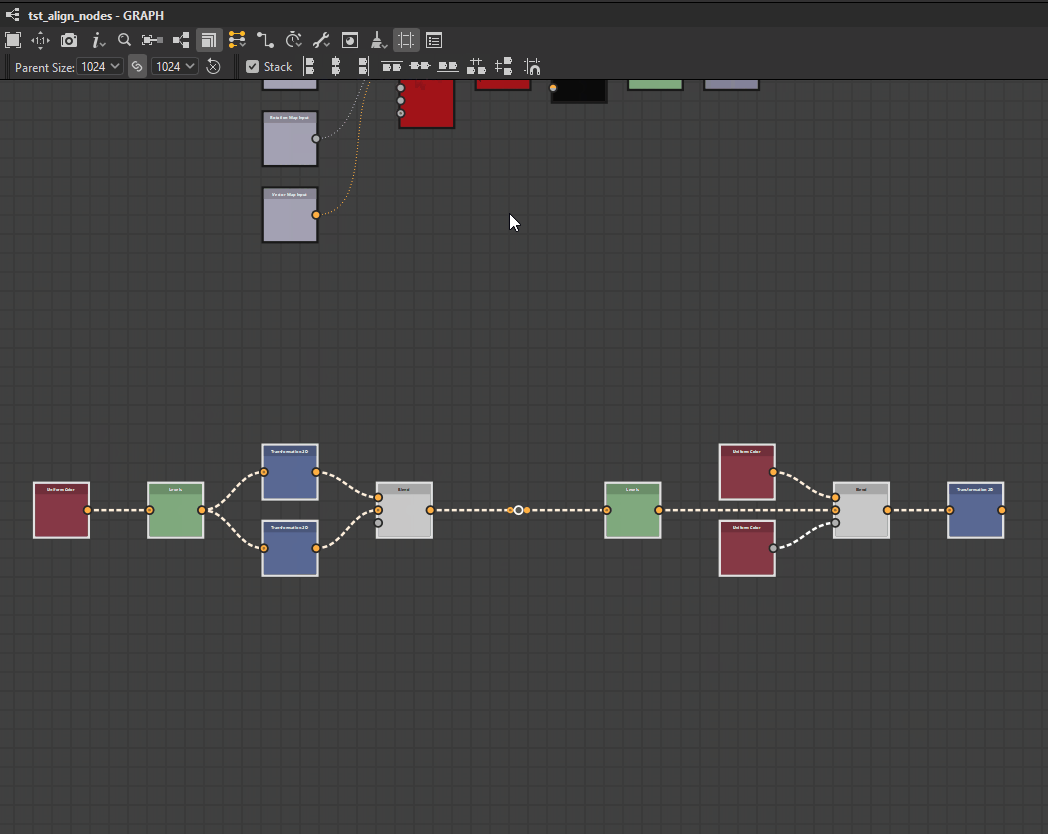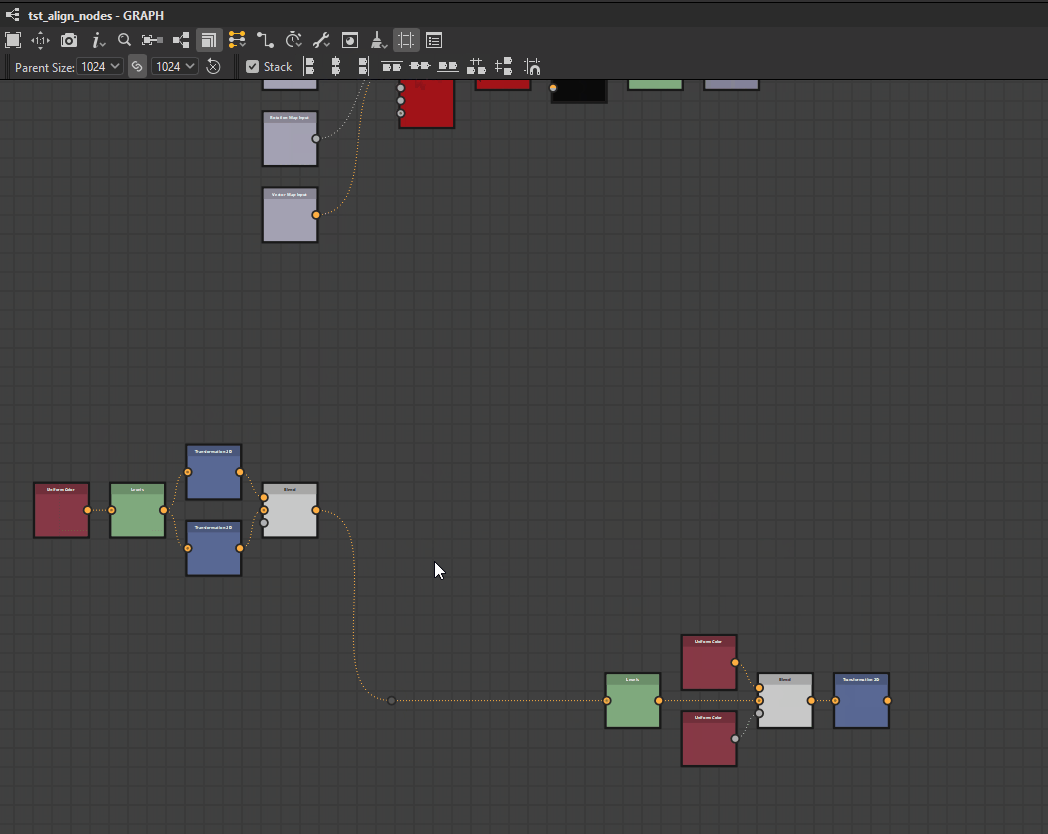

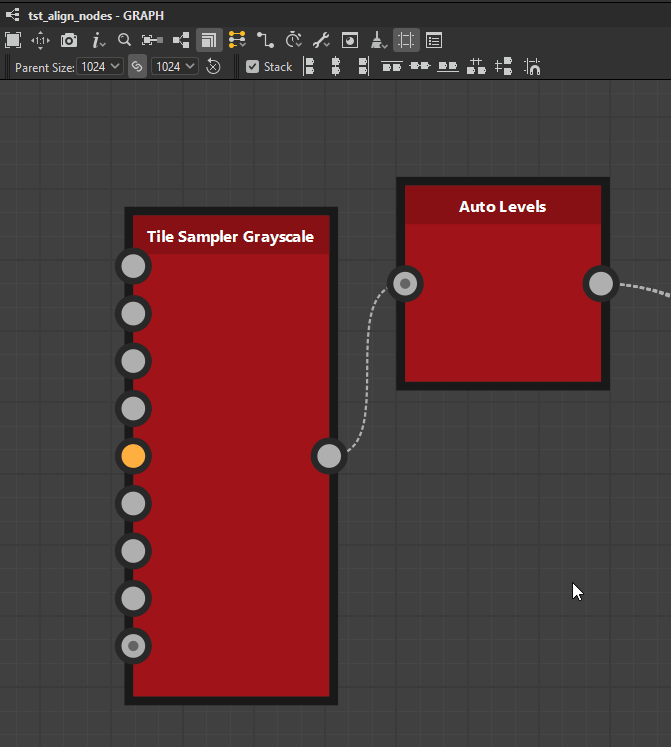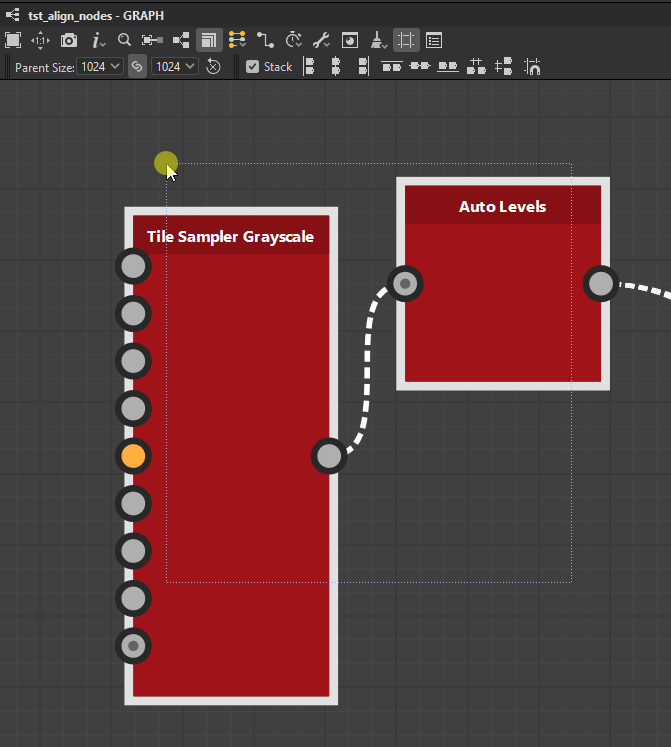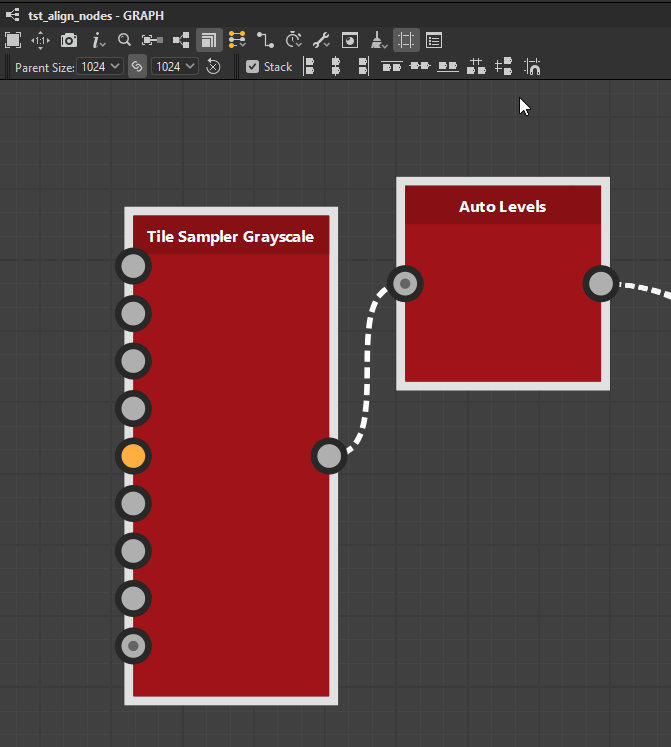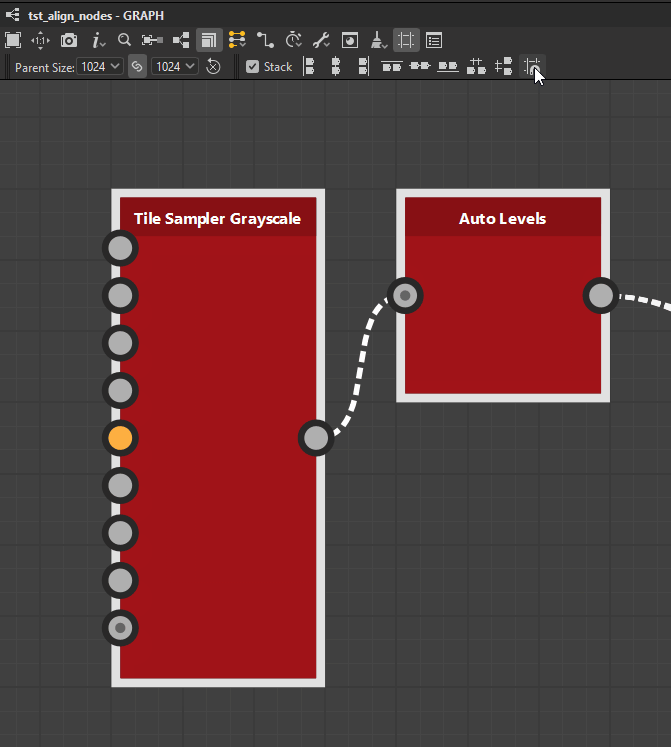
Nodes can be distributed evenly between the nodes at each extremes of the current selection on the desired axis.
![]() Horizontally: Nodes are distributed evenly between the leftmost and rightmost nodes in the selection.
Horizontally: Nodes are distributed evenly between the leftmost and rightmost nodes in the selection.
![]() Vertically: Nodes are distributed evenly between the topmost and lowermost nodes in the selection.
Vertically: Nodes are distributed evenly between the topmost and lowermost nodes in the selection.
The distributions aim for even spacing between the nodes, regardless of their size.
When multiple nodes have their centers perfectly aligned on the selected axis, they remain and are treated as one in the distribution. The largest of the aligned nodes is used for computing the even spacing.
Note that when the total size of the selected nodes is greater than the space available on the selected axis, overlapping may occur.
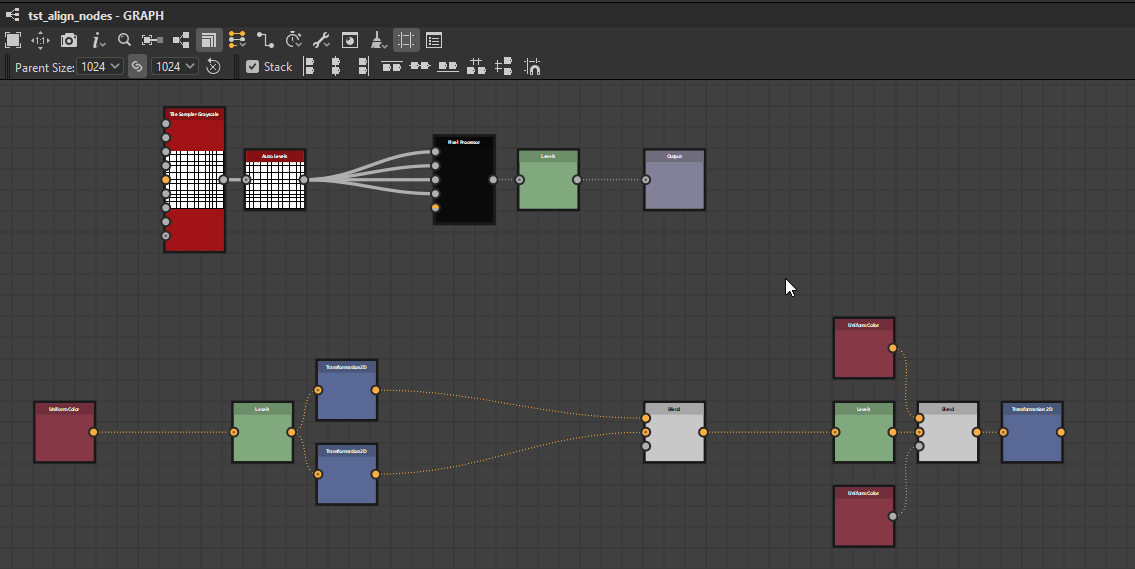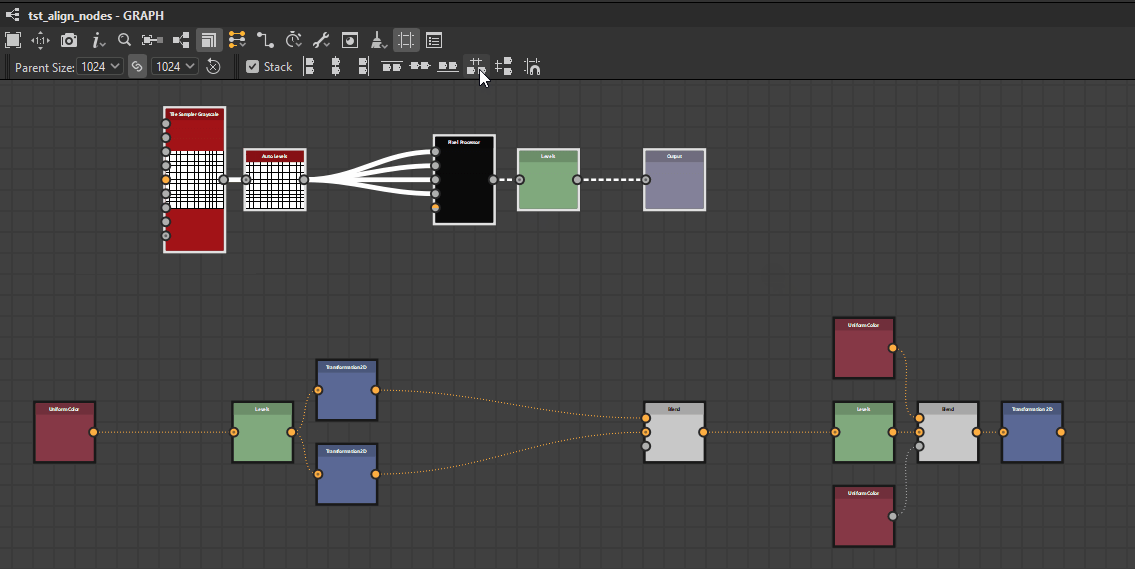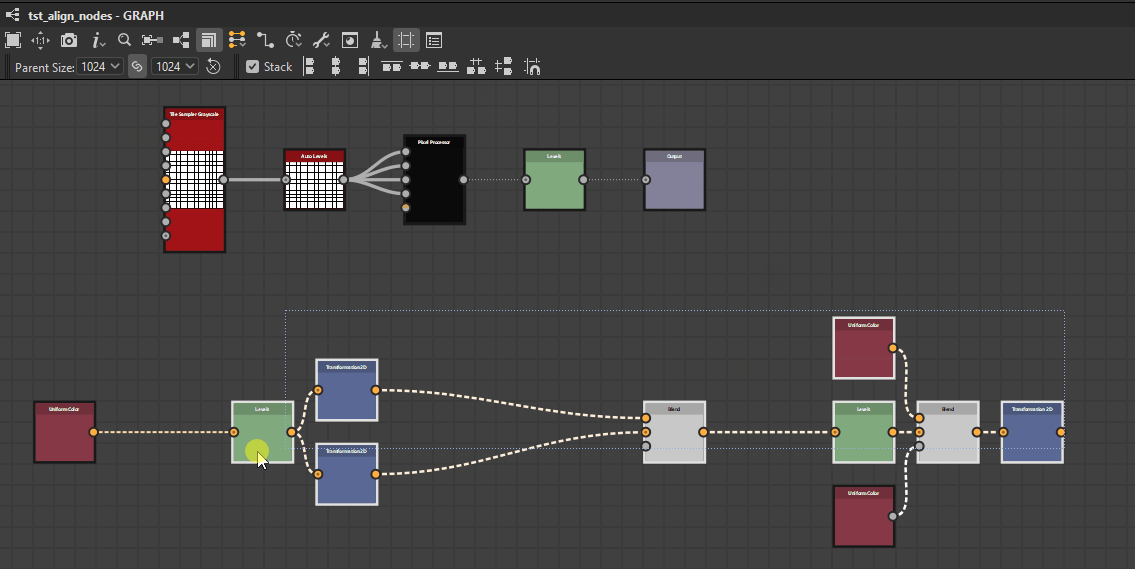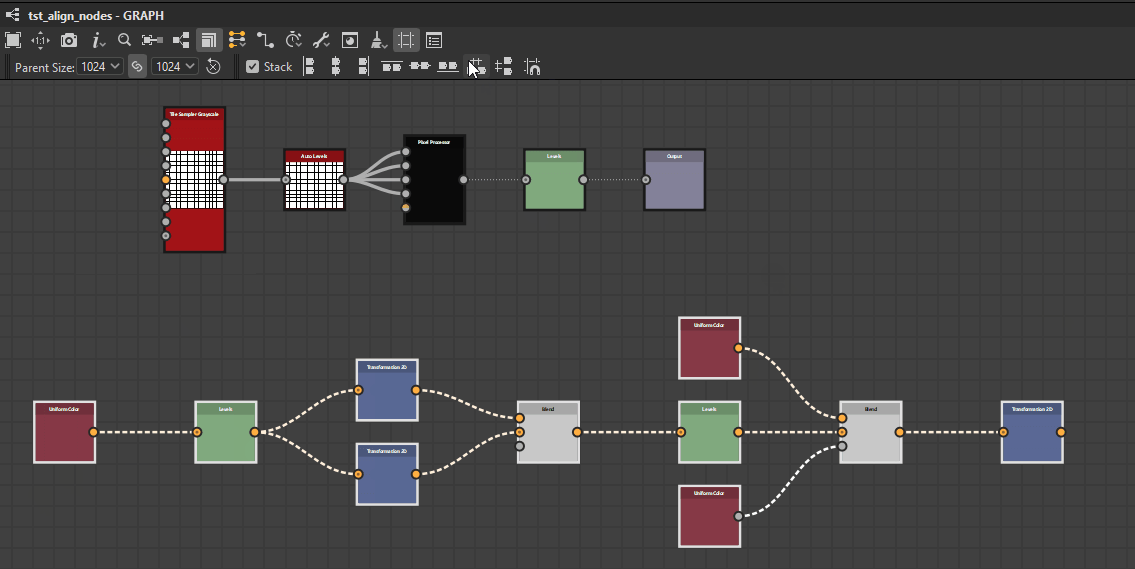

Horizontally
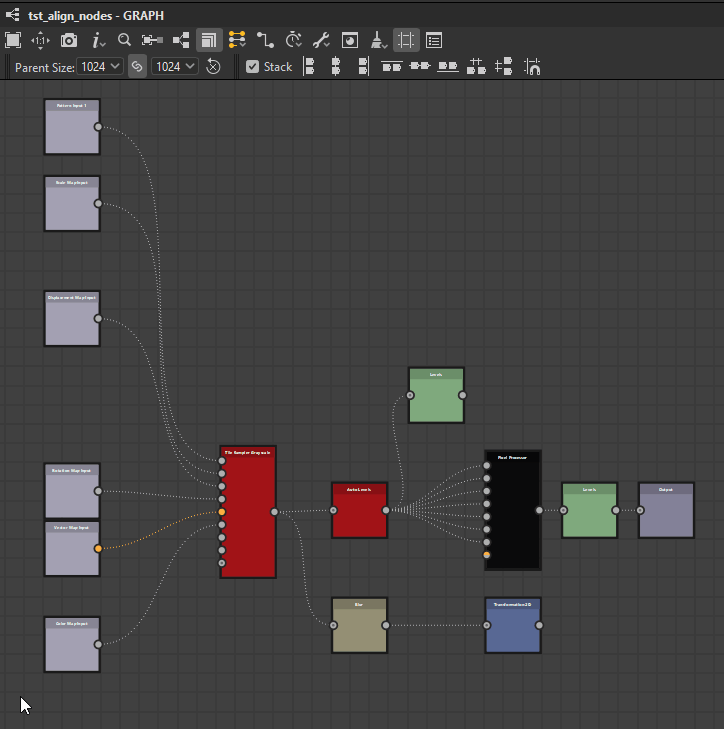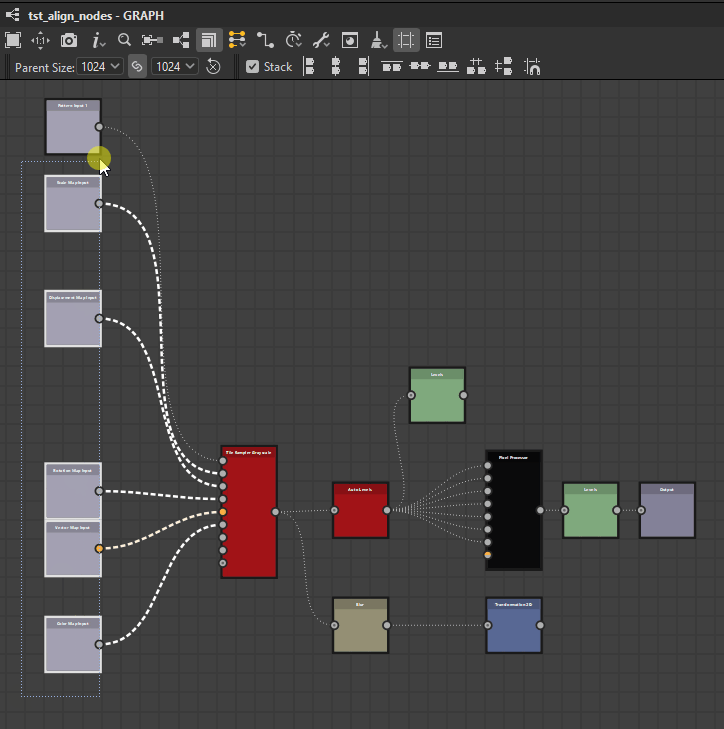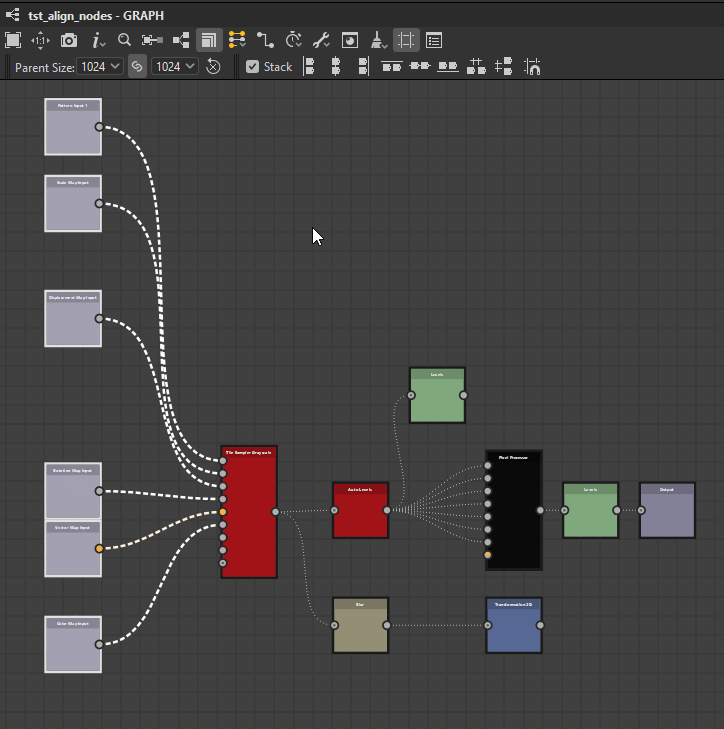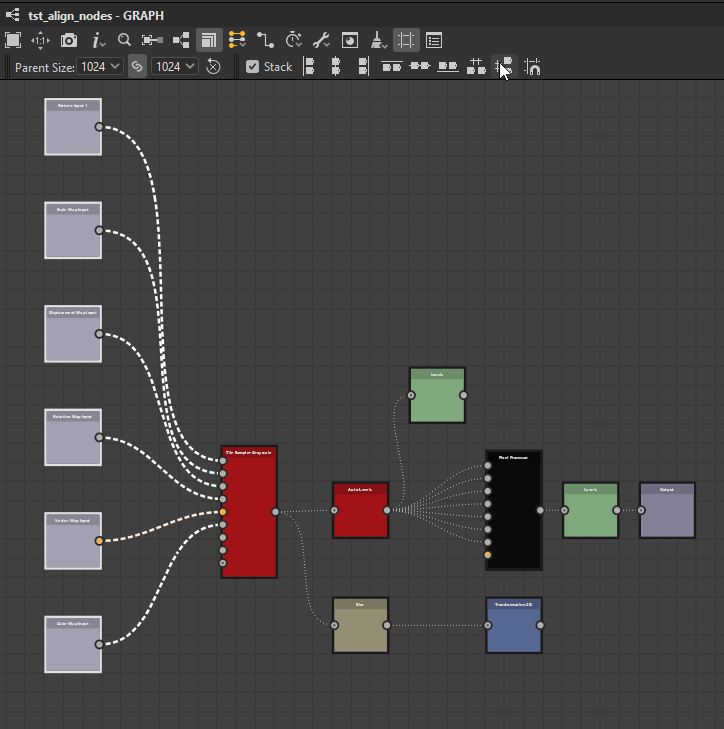

Vertically